This article will guide you through writing effective unit tests for your Spring Boot REST services.
To keep things simple and practical, we’ll start by creating a few basic REST endpoints using a sample Spring Boot project. Once the services are ready, we’ll explore how to write clean, reliable unit tests for them.
You will learn
- What Unit Testing is and why it matters
- How to create a GET REST Service to retrieve the courses registered by a student
- How to write a Unit Test for the GET REST Service
- How to create a POST REST Service to register a course for a student
- How to write a Unit Test for the POST REST Service
Tools you will need
- Maven 3.0+ – Build and dependency management tool
- An IDE of your choice – Eclipse, IntelliJ IDEA, or any other Java IDE
- JDK 17+ – Java Development Kit to compile and run the application
Complete Maven Project With Code Examples
You can find all the code examples in our GitHub repository:
https://github.com/in28minutes/in28minutes.github.io/tree/master/code-zip-files
- REST Services with Unit and Integration Tests
👉 Download:Website-springbootrestservices-simplerestserviceswithunitandintegrationtests.zip
Unit Testing
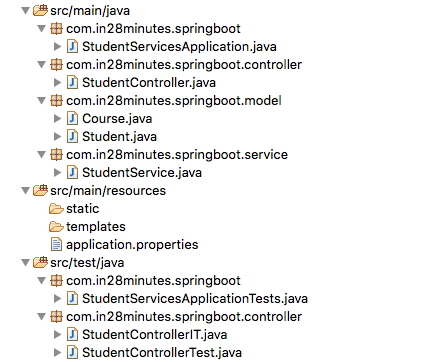
The following screenshot shows the Eclipse project structure with all the files we will create as part of this tutorial.
We will cover:
- Writing a simple GET REST Service and its unit test
- Writing a POST REST Service and its unit test

Writing Unit Tests for StudentController
The StudentController exposes two service methods — GET and POST.
We will create unit tests for both of these methods.
In the unit tests:
- The
StudentServicedependency will be mocked using Mockito. - We will use the MockMvc framework to launch only the
StudentController.
⚡ Key Principle:
A critical aspect of unit testing is limiting the scope.
Here, we only want to test the logic inside StudentController, without involving the actual StudentService implementation or other layers.
Overview
In this guide, we will walk through the process of building and testing a simple Spring Boot REST API.
The steps we will follow are:
-
Bootstrap the Project
Use Spring Initializr to quickly set up the base project. -
Implement the Business Service
Create theStudentServiceclass to provide business logic for our API. - Build the REST API
Develop theStudentController:- First, implement the GET endpoints.
- Then, implement the POST endpoint.
- Write Unit Tests
Use Mockito and MockMvc to unit test theStudentController.
Bootstrap REST Services Application with Spring Initializr
Spring Initializr is an excellent tool for bootstrapping Spring Boot projects with just a few clicks.
With Spring Initializr, you can quickly generate a project structure by selecting:
- Group:
com.in28minutes.springboot - Artifact:
student-services - Dependencies:
- Spring Web
- Spring Boot Actuator
- Spring Boot DevTools
Once generated, download the project, unzip it, and import it into your favorite IDE (Eclipse, IntelliJ, or VS Code).
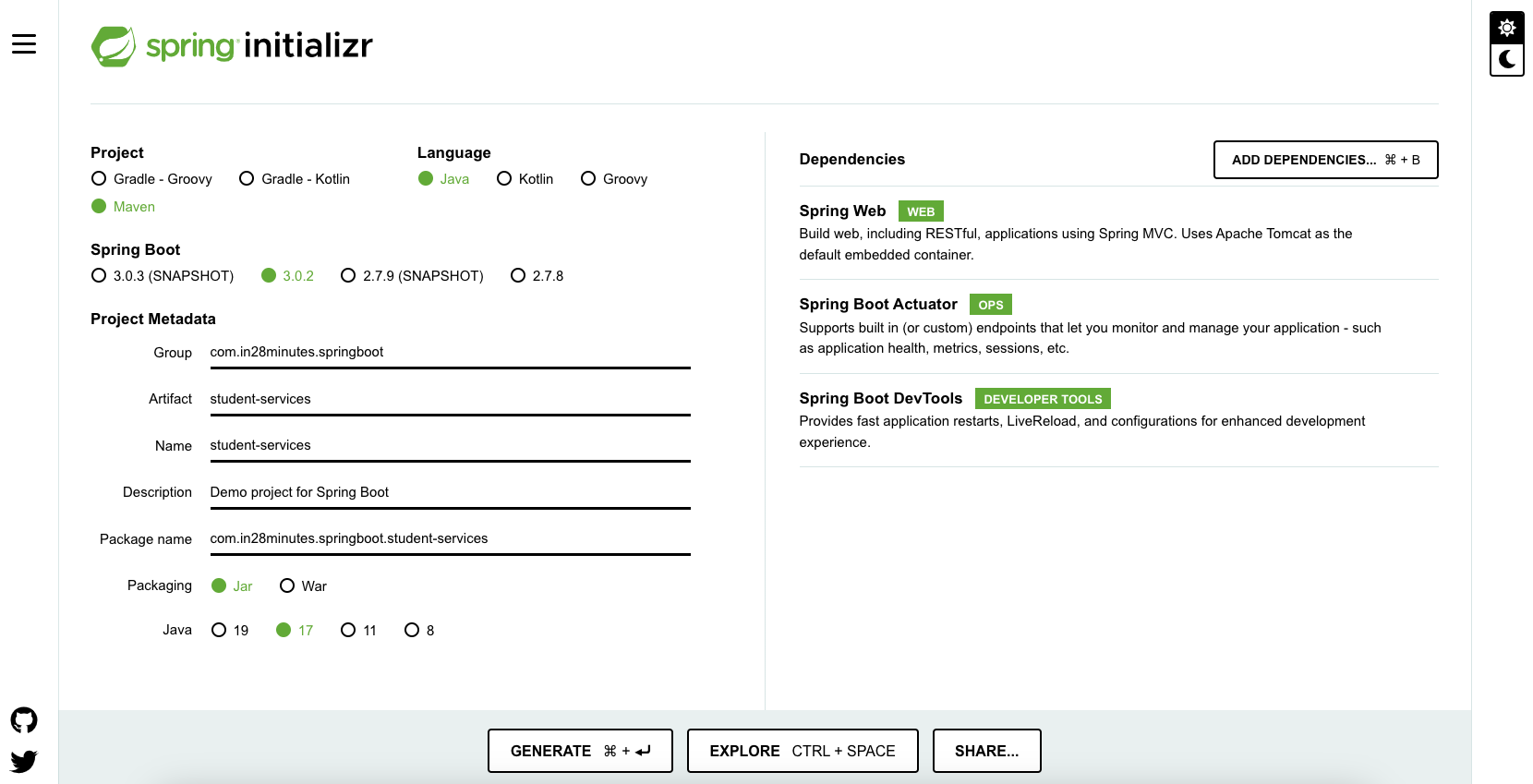
As shown in the image above, follow these steps to create your project:
- Launch Spring Initializr and choose the following:
- Group:
com.in28minutes.springboot - Artifact:
student-services - Dependencies:
- Spring Web
- Spring Boot Actuator
- Spring Boot DevTools
- Group:
- Click Generate Project to download the starter project.
- Import the project into Eclipse (File → Import → Existing Maven Project).
- To explore and understand all the files generated by Spring Initializr, you can refer here.
Adding Business Services to Your Application
Every application needs data. In this example, instead of connecting to a real database, we’ll use an ArrayList as an in-memory data store.
- A student can enroll in multiple courses.
- A course has an
id,name,description, and a list ofstepsto complete the course. - A student has an
id,name,description, and a list of registered courses.
We’ll implement a StudentService that provides the following methods:
public List<Student> retrieveAllStudents()– Retrieve details for all studentspublic Student retrieveStudent(String studentId)– Retrieve details of a specific studentpublic List<Course> retrieveCourses(String studentId)– Retrieve all courses a student is registered forpublic Course retrieveCourse(String studentId, String courseId)– Retrieve a specific course for a studentpublic Course addCourse(String studentId, Course course)– Add a new course for an existing student
You can find the actual implementation of the service and models in these files:
src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/model/Course.javasrc/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/model/Student.javasrc/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/service/StudentService.java
Adding a Couple of GET Operations
The StudentController exposes two GET REST endpoints:
private final StudentService studentService;
public StudentController(StudentService studentService) {
this.studentService = studentService;
}
- Uses Spring Dependency Injection to wire the
StudentServiceinto the controller. @GetMapping("/students/{studentId}/courses")– Retrieves all courses for a given student (studentIdis passed as a path variable).@GetMapping("/students/{studentId}/courses/{courseId}")– Retrieves details of a specific course (courseId) for a student.@PathVariable String studentId– Maps the value ofstudentIdfrom the URI to this parameter.
package com.in28minutes.springboot.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.in28minutes.springboot.model.Course;
import com.in28minutes.springboot.service.StudentService;
@RestController
public class StudentController {
private final StudentService studentService;
public StudentController(StudentService studentService) {
this.studentService = studentService;
}
@GetMapping("/students/{studentId}/courses")
public List<Course> retrieveCoursesForStudent(@PathVariable String studentId) {
return studentService.retrieveCourses(studentId);
}
@GetMapping("/students/{studentId}/courses/{courseId}")
public Course retrieveDetailsForCourse(@PathVariable String studentId,
@PathVariable String courseId) {
return studentService.retrieveCourse(studentId, courseId);
}
}
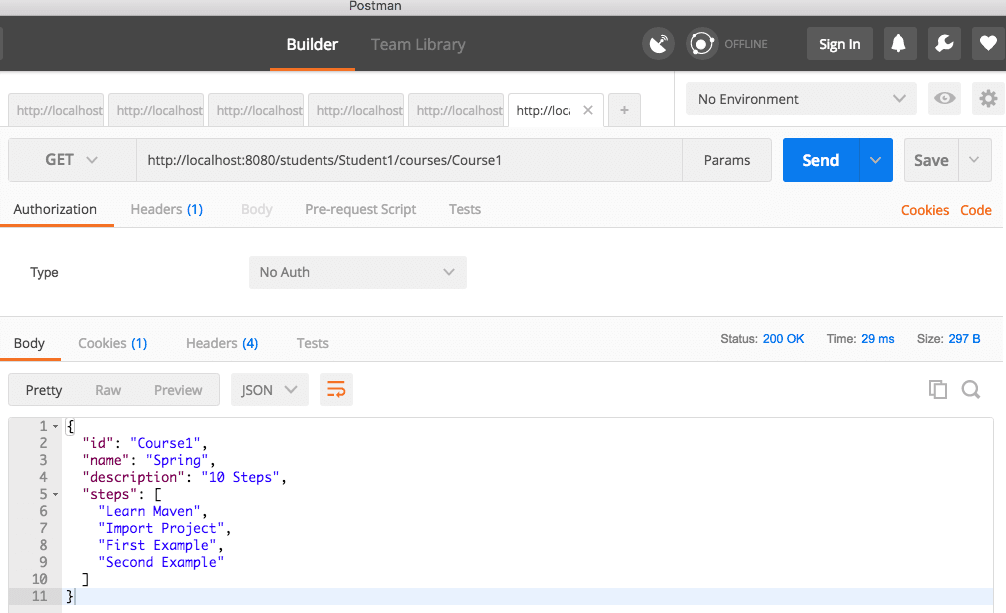
Executing the Http Get Operation Using Postman
We will fire a request to http://localhost:8080/students/Student1/courses/Course1 to test the service. Response is as shown below.
{
"id": "Course1",
"name": "Spring",
"description": "10Steps",
"steps": [
"Learn Maven",
"Import Project",
"First Example",
"Second Example"
]
}
Below screenshot demonstrates how to execute this GET operation using Postman — a popular tool for testing RESTful services.
Add spring-security-test for disabling security in unit tests
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Unit Testing Http Get Operation
Unit Testing a Spring MVC Controller
When unit testing a REST service, we want to launch only the relevant controller and the associated MVC components.
The annotation @WebMvcTest is used for this purpose. It focuses the test exclusively on Spring MVC components. Using this annotation disables full auto-configuration and loads only the configuration relevant for MVC tests.
Key components in our test setup:
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)- Registers Spring extensions with JUnit 5.
- Integrates the Spring TestContext Framework into JUnit Jupiter.
- Supports annotated arguments in constructors, test methods, and lifecycle methods (
@BeforeAll,@BeforeEach,@AfterAll,@AfterEach).
@WebMvcTest(value = StudentController.class)- Used to unit test Spring MVC components.
- Launches only
StudentControllerfor testing. - No other controllers or mappings are started.
@Autowired private MockMvc mockMvc- Entry point for server-side Spring MVC test support.
- Allows executing HTTP requests against the test context.
@MockBean private StudentService studentService- Mocks the
StudentServiceand injects it intoStudentController. - Ensures the unit test only focuses on controller behavior.
- Mocks the
Mockito.when(studentService.retrieveCourse(Mockito.anyString(), Mockito.anyString())).thenReturn(mockCourse)- Mocks the behavior of
retrieveCourse()to return a predefinedmockCourse.
- Mocks the behavior of
MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/students/Student1/courses/Course1").accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)- Creates a GET request to the specified URI with an
Acceptheader ofapplication/json.
- Creates a GET request to the specified URI with an
mockMvc.perform(requestBuilder).andReturn()- Executes the request using
MockMvcand returns the response.
- Executes the request using
JSONAssert.assertEquals(expected, result.getResponse().getContentAsString(), false)- Uses
org.skyscreamer.jsonassert.JSONAssertto assert JSON responses. - Passing
strict=falseallows partial checks without requiring all fields to match.
- Uses
package com.in28minutes.springboot.controller;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.mockito.Mockito;
import org.skyscreamer.jsonassert.JSONAssert;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockBean;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MvcResult;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.RequestBuilder;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import com.in28minutes.springboot.model.Course;
import com.in28minutes.springboot.service.StudentService;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@WebMvcTest(value = StudentController.class)
@WithMockUser
public class StudentControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@MockBean
private StudentService studentService;
Course mockCourse = new Course("Course1", "Spring", "10Steps",
Arrays.asList("Learn Maven", "Import Project", "First Example", "Second Example"));
String exampleCourseJson = "{\"name\":\"Spring\",\"description\":\"10Steps\",\"steps\":[\"Learn Maven\",\"Import Project\",\"First Example\",\"Second Example\"]}";
@Test
public void retrieveDetailsForCourse() throws Exception {
Mockito.when(studentService.retrieveCourse(Mockito.anyString(),
Mockito.anyString())).thenReturn(mockCourse);
RequestBuilder requestBuilder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get(
"/students/Student1/courses/Course1").accept(
MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
MvcResult result = mockMvc.perform(requestBuilder).andReturn();
System.out.println(result.getResponse());
String expected = "{\"id\":\"Course1\",\"name\":\"Spring\",\"description\":\"10 Steps\"}";
// {"id":"Course1","name":"Spring","description":"10 Steps, 25 Examples and 10K Students","steps":["Learn Maven","Import Project","First Example","Second Example"]}
JSONAssert.assertEquals(expected, result.getResponse()
.getContentAsString(), false);
}
}
Adding Http POST Operation
Implementing a HTTP POST Operation
An HTTP POST operation should return a 201 Created status when the resource is successfully created.
Key components of the POST implementation:
-
@PostMapping("/students/{studentId}/courses")
Maps the URL to handle POST requests for adding a course to a student. -
@RequestBody Course newCourse
Binds the JSON body of the request to aCourseobject. -
ResponseEntity.created(location).build()
Returns a 201 Created status and sets the Location header pointing to the URI of the newly created resource.
Example:
When adding a course to Student1, the POST request might look like:
@PostMapping("/students/{studentId}/courses")
public ResponseEntity<Void> registerStudentForCourse(
@PathVariable String studentId, @RequestBody Course newCourse) {
Course course = studentService.addCourse(studentId, newCourse);
if (course == null)
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
URI location = ServletUriComponentsBuilder.fromCurrentRequest().path(
"/{id}").buildAndExpand(course.getId()).toUri();
return ResponseEntity.created(location).build();
}
Executing the Http POST Operation
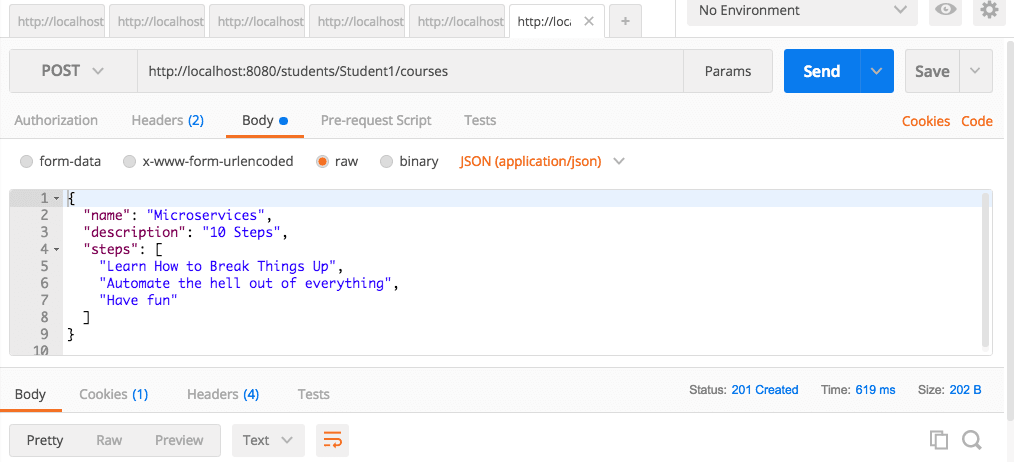
An example request is shown below. It provides all of the information needed to enrol a student for a course.
{
"name": "Microservices",
"description": "10Steps",
"steps": [
"Learn How to Break Things Up",
"Automate the hell out of everything",
"Have fun"
]
}
Executing the HTTP POST Operation Using Postman
The image below demonstrates how to perform this POST operation using Postman — my preferred tool for testing REST services.
Steps to follow:
- Go to the Body tab in Postman.
- Select raw.
- From the dropdown menu, choose JSON.
- Copy and paste the JSON request (shown above) into the body.
- Click Send to execute the POST request.
If successful, the server will return a 201 Created status along with the location of the newly created resource in the response headers.
The URL we use is http://localhost:8080/students/Student1/courses.
Writing Unit Test for the Http POST Operation
Unit Testing the HTTP POST Operation
In the unit test, we want to send a POST request to /students/Student1/courses and validate that:
- The HTTP status returned is 201 Created.
- The Location header contains the URI of the newly created resource.
Key components in the test:
-
MockMvcRequestBuilders.post("/students/Student1/courses").accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
Creates a POST request with anAcceptheader set toapplication/json. -
content(exampleCourseJson).contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
Sets the request body toexampleCourseJsonand specifies the content type as JSON. -
assertEquals(HttpStatus.CREATED.value(), response.getStatus())
Verifies that the response status is 201 Created. -
response.getHeader(HttpHeaders.LOCATION)
Retrieves the Location header from the response. You can then assert that it contains the URI of the newly created course.
@Test
public void createStudentCourse() throws Exception {
var mockCourse = new Course("1", "Smallest Number", "1", Arrays.asList("1", "2", "3", "4"));
// studentService.addCourse to respond back with mockCourse
Mockito.when(studentService.addCourse(Mockito.anyString(),
Mockito.any(Course.class))).thenReturn(mockCourse);
// Send course as body to /students/Student1/courses
RequestBuilder requestBuilder = MockMvcRequestBuilders
.post("/students/Student1/courses")
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).content(exampleCourseJson)
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
MvcResult result = mockMvc.perform(requestBuilder).andReturn();
MockHttpServletResponse response = result.getResponse();
assertEquals(HttpStatus.CREATED.value(), response.getStatus());
assertEquals("http://localhost/students/Student1/courses/1",
response.getHeader(HttpHeaders.LOCATION));
}