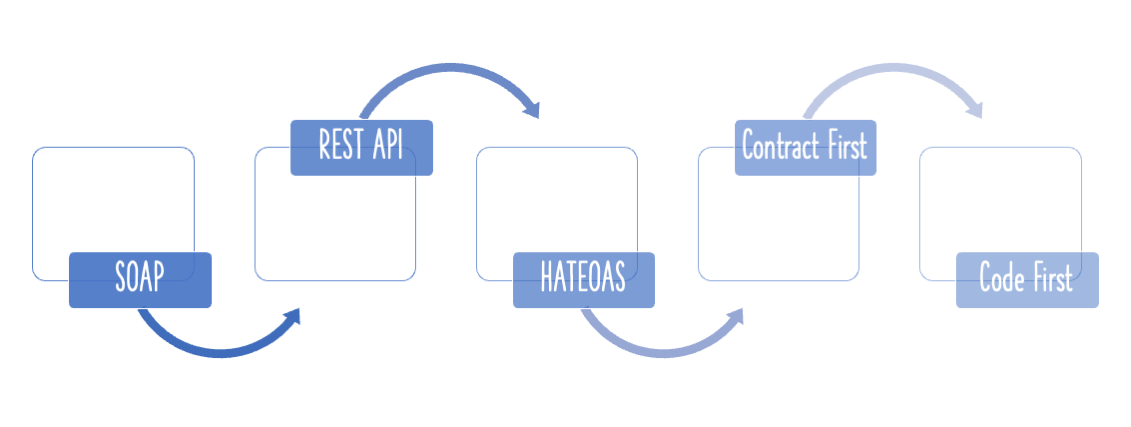
We love all our 100,000 learners. We want to help you in every way possible.
We do not want you to get stuck because of a simple error.
This 50 page troubleshooting guide and faq is our way of thanking you for choosing to learn from in28Minutes.
How to use this guide?
1. Ensure You Have The Recommended Versions of Tools/Versions
First of all - Make sure you are using the right versions. Here is the recommended versions and errors if you don’t use them:
| Recommended Version | Errors with other versions | More Details |
|---|---|---|
| Java 8 | Unsupported major.minor version 52.0 | Basics |
| Eclipse Java EE Oxygen | org.codehaus.plexus.archiver.jar.Manifest.write (java.io.PrintWriter) | Basics |
| Spring Boot 2.3.1.RELEASE | Maven download issues. Hal Browser and Spring Boot Actuator are not working! | Configure 2.3.1.RELEASE |
2. Highly Probable Errors
Problems a high proportionate of our learners face.
| Error | Solution Reference |
|---|---|
| Compilation failure [ERROR] No compiler is provided in this environment. Perhaps you are running on a JRE rather than a JDK? | Configure Eclipse to use JDK |
| Could not transfer artifact | Check Maven Configuration |
| Hal Browser and Spring Boot Actuator are not working | Configure Spring Boot Version 2.3.1.RELEASE |
| H2 Embedded Database - Cannot find tables | Use the right database name |
| Failed to load class (or)Could not find or load main class or Failed to read Class-Path attribute from manifest | Redownload artifacts with Maven |
| java.net.BindException: Address already in use: JVM_Bind | Stop 8080 or Use Other Port |
| No mapping found for HTTP request | Check your component scan configuration |
| No qualifying bean of type | Check your component scan configuration |
| java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/springframework/web/cors/CorsConfigurationSource | Solution |
| Unable to find setter method for attribute commandName | Use modelAttribute |
3. Go for the complete list
If you are facing a exception or an error
- Try searching with complete exception text
- Try searching with a substring
- Try searching with name of exception
- Try searching with the direct cause of exception
- Try searching for the framework and browse through the FAQ
If the troubleshooting guide does not help you solve your specific problem, raise a pull request with the problem and solution to improve the troubleshooting guide.
If you see a bug in the troubleshooting guide, raise a pull request to improve the troubleshooting guide.
If you are here for fun, continue reading.
This will be the best 20 minute investment you made in your programming career. You get an understanding of how you can troubleshoot a wide variety of issues.
Happy Troubleshooting.
- Basics
- Tip : Ensure you have the right version of Java Installed
- Tip : Ensure you have the right version of Eclipse Installed
- Tip : Troubleshooting Embedded Maven in Eclipse
- Error : You are not using a JDK
- Error : You are not connected to internet or You are behind a proxy!
- Error : Files Downloaded by Maven are Corrupt
- Error : org.codehaus.plexus.archiver.jar.Manifest.write(java.io.PrintWriter)
- Error : Unsupported major.minor version 52.0
- Tip : Your Project Maven configuration should be configured to compile at Java 8
- Error : On Maven > Update Project, Java 1.4 is auto selected
- Error : Changes you made are not reflected
- Q : What should I do when some other application is using default port 8080?
- Q : Do I need to install Tomcat seperately for this course?
- Q : Why do we use this specific project structure in all our courses?
- Q : What software do you use for your diagrams or Mind Maps?
- Q : How to debug the application?
- Q : How do I configure auto restarting the server whenever source code changes?
- Q : Can I use jboss instead of tomcat server?
- Q : How to get the projects to run in Tomcat 8 or 9?
- Maven
- Q : Why Maven?
- Q : What is ArtifactId and GroupId?
- Q : How to know the exact string and name of a dependency and its artifactid?
- Q : What’s the difference between scope and phase?
- Q : Maven - How did a specific jar end up in our deployable?
- Q : What is a SNAPSHOT as in 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT?
- Q : What is difference between runtime and provided scopes?
- Q : How can you always exclude a specific jar using Maven Exclusions?
- Tip : Example of a multi layered maven project
- Error : java.lang.ClassNotFoundException
- Q : Why are we not using Gradle?
- Eclipse
- Intellij and/or Mac
- Q : How to install Maven on MAC OS X?
- Q : How do I import a Maven project into Intellij?
- Q : How do I create and run unit tests (JUnit) with Intellij?
- Error : I’m having a problem running jsps with Spring Boot in Intellij. What should I do?
- Q : Why does Hot reload not work with Spring Boot DevTools and Intellij?
- Spring
- Q : What is the need for a Component Scan?
- Q : How do you define a Component Scan?
- Q : How do I solve Errors related to Component Scan?
- Q : What is the difference between @Component and @ComponentScan?
- Q : How do I choose between Spring and CDI?
- Q : Why do we write a lot of unit tests in the Spring Master Class course?
- Q : What is the use of an @Bean annotation?
- Q : What is the difference between @Bean and @Component?
- Q : What is the difference between @Component, @Service and @Repository annotations?
- Q : Can we use @Component annotation instead of @Service for Business Services?
- Q : What is the difference between web.xml and the Spring Context - servlet.xml?
- Q : Should we use XML or Annotation based wiring?
- Q : Can we do autowiring with Non Setter and Non Constructor Methods?
- Q : Where should we use Checked Exceptions?
- Q : What is the difference between Cross Cutting Concerns and AOP?
- Q : What is difference between IOC and Application Context?
- Q : What is the difference between classPathXmlApplicationContext and annotationConfigApplicationContext ?
- Q : When @Around aspect is introduced the value returned by@AfterReturning is lost. Why is this happening?
- Q : How do you use which autowiring type to use - @Primary or @Qualifier?
- Q : What are the New Features in Spring Framework 5.0?
- Q : What are the possible reasons of preDestroy not being called?
- Q : Compare Application Context vs IOC Container vs Web Container vs EJB Container
- Notes : Notes from Rodolfo
- Q : How do we inject different bean depending on the configuration in application.properties?
- Error : Log4j problems with Spring 5!
- Q : What is the minimum baseline Java Version for Spring Boot 2 and Spring 5?
- Error : Getting SLF4J errors and not getting logger output in Lecture 41 - Step 19?
- Error : No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath
- JSP Servlets and Spring MVC
- Q : What is the difference between @Controller and @RestController?
- Q : Why is there no context root in the request url for each web application?
- Q : What does tomcat7:run exactly mean?
- Q : How is the URL decided with Spring MVC?
- Error : No plugin found for prefix ‘tomcat7’ in the current project
- Q : Is this kind of Tomcat server usage what is commonly referred to as “Embedded Tomcat Server” ?
- Q : How do we handle errors to non existing URL Paths with Spring MVC?
- Q : How do we configure a welcome page?
- Q : Why do we teach JSP and Servlets in the first section of Spring MVC Course?
- Q : Why do we use @ResponseBody sometimes and ResponseEntity some other times?
- Q : What is difference between Spring 5 and Spring 4 in terms of developing web application in the course? Does it matter if a new version is used ?
- Q : What is the difference between Filters, Listeners and Interceptors?
- Q : What is the difference between ModelMap and ModelAndView?
- Q : What is the difference between model.put() and model.addAttribute()?
- Q : How do you pass values from Java Controller to JSP?
- Q : What is Form Binding?
- Q : What is WEB-INF exactly? Why so we need it?
- Q : Why do we use Hibernate Validator?
- Q : Are Model objects specific to a request?
- Q : The groupid for jstl jar is jstl and not javax.servlet
- Q : Why are we using request GET method for “delete-todo” request?
- Q : Why do we need xmlns hyperlinks? like http://www.springframework.org/schema/bean
- Error : View is not resolving to a JSP
- Q : How to use own CSS with Spring MVC?
- Q : Where should we place our static (css, js, html) resources in a Spring MVC application?
- Q : How to add a custom login page in Spring Security?
- Q : How can you authenticate by connecting to a database with Spring Security?
- Q : Why is request method POST recommended compared to GET for sensitive data?
- Q : We use ${todo.done} in JSP even though the name of the field in Todo.java is isDone. Shouldn’t we be using ${todo.isDone}?
- Error : After adding security dependencies - java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AutoProxyUtils.determineTargetClass
- Q : How do I ensure that session attributes are not part of the request url?
- Error : Spring Security - java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/springframework/web/cors/CorsConfigurationSource
- Error : Unable to find setter method for attribute commandName
- Q : Can I have multiple parameters with the same name in a request?
- Error : java.lang.IllegalStateException: Neither BindingResult nor plain target object for bean name ‘todo’ available as request attribute
- Error : Caused by: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: The servlets named [com.in28minutes.LoginServlet] and [webapp.LoginServlet] are both mapped to the url-pattern [/login.do] which is not permitted
- Q : How is server picking up index.html and index.jsp even when they are not configured in web.xml?
- Q : What is the benefit of using view resolver?
- Q : What is @ControllerAdvice?
- Q : What Request method should be used for updating user details?
- Q : What is the difference between put and patch request methods?
- Spring Boot
- Q : What should be the first things I read about Spring Boot?
- What is the minimum baseline Java Version for Spring Boot 2 and Spring 5?
- Q : Is Spring Initializr the only way to create Spring Boot Projects?
- Q : Why am I not seeing code completion when updating application.properties in Eclipse?
- Q : Why do we need spring-boot-maven-plugin?
- Q : Devtools helps me to restart the server automatically. But, I have a problem. The browser page is not auto refreshed.
- Q : What and Why Embedded Servers?
- Q : How can I add custom JS code with Spring Boot?
- Error : HAL browser gives me unauthorized error - Full authentication is required to access this resource.
- Error : Hal Browser and Spring Boot Actuator are not working
- Q : How does path=”users”, collectionResourceRel=”users” work with Spring Data Rest?
- Q : What is importance of {id} in ServletUriComponentsBuilder.fromCurrentRequest().path(”/{id}”).buildAndExpand(returnQuestion.getId()).toUri();
- Error : java.lang.ClassCastException: org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationReadyEvent cannot be cast
- Q : What is difference between Spring 5 and Spring 4 in terms of developing web application in the course? Does it matter if a new version is used ?
- Q : Why am I seeing an extra dialogue asking me to “Select Java Application Type” when I launch a Spring Boot Application?
- Q : What happens in the background when a Spring Boot Application is “Run as Java Application”?
- Q : Can we use jetty instead of tomcat in spring-boot-starter-web?
- Error : Failure to transfer org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-parent:pom:2.3.1.RELEASE from https://repo.spring.io/snapshot
- Q : Why do we configure Spring Snapshot and milestone repositories?
- Error : java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Sources must not be empty
- Q : Can i use spring boot dev tools for a non spring boot project?
- Q : What is the difference between Static and Dynamic filtering?
- Error : No message found under code ‘good.morning.message’ for locale ‘us’.
- Q : How to generate a WAR file with Spring Boot?
- Q : How to deploy to a different server with with Spring Boot?
- Q : What is the difference between RequestMapping and GetMapping?
- Q : Why do we recommend not to use Spring Data Rest in real world applications?
- Q : How do I change the package name of a project in Spring Initializer?
- Q : Where can I find the complete list of properties that can be configured in application.properties?
- Hibernate, JPA and In-memory Database
- Q : What is the difference between JPA and Hibernate?
- Q : Compare Entity Manager vs SessionFactory
- Q : In which layer, should the boundary of a transaction start?
- Q : HQL vs JPQL
- Q : What are the dependencies need to start up an in memory database H2 with Spring Boot?
- Q : How is Hibernate chosen as the default implementation for JPA without any configuration?
- Q : Why H2? And how does it work?
- Q : Where is the database connection info specified? How does it know to automatically connect to H2?
- Q : How do we connect to a external database like MSSQL or oracle?
- Q : What is the default h2 database name configured by Spring Boot? Why is the default database name testdb?
- Q : What happens if H2 is not in the classpath?
- Q : Why the data lost between restart?
- Error : Table is not created automatically in h2 embedded db or I’m unable to see the tables
- Error : H2 Console is not Launched up?
- Q : How did the insert query from data.sql run at application startup?
- Q : How to define a Composite Primary Key or a Composite ID?
- Q : Why should we annotate EntityManager with @PersistenceContext and not just @Autowired?
- Q : How can we connect to Multiple Databases using Spring Boot?
- Q : How did JdbcTemplate achieve connection details?
- Q : Can you give an example for ReadOnly as true in Transaction management?
- Error : org.hibernate.loader.MultipleBagFetchException
- Error : BeanCreationException - java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: At least one JPA metamodel must be present
- Q : Is it mandatory to specify @Repository on a repository which is extending JPARepository?
- Q : JPA and Hibernate Course - Notes from Rodolfo
- Q : How can we use a mysql database for running the application and use inmemory database H2 for unit tests?
- Q : When is any primary or an id field annotated with @GeneratedValue autogenerated? Why are we passing the value for id in data.sql?
- Q : Field dao in SpringRestController required a bean of type ‘CustomerDAO’ that could not be found. Consider defining a bean of type ‘CustomerDAO’ in your configuration.
- Error : Detached object passed to persist
- Error : java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: javax/wsdl/extensions/ExtensibilityElement
- Q : How do authentication with jwt to service REST??
- Unit Testing
- You and in28Minutes
Basics
This video can help with simple troubleshooting - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZZw8XNz5N-c&t=6s
Tip : Ensure you have the right version of Java Installed
Recommended Java Version
- Do not use Java 9. My recent tests show a few compatibility issues with Spring Boot 2.0+. Let’s wait for these get resolved
- Java 8 for Spring Boot 2.0+ or Spring 5.0+
- Java 7/Java 8 for earlier versions
Java JDK Version in Eclipse You can use JavaSE-1.8 to develop Java 8 and any lower version of Java applications. You can control the version of an application through maven.
https://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-compiler-plugin/examples/set-compiler-source-and-target.html
Tip : Ensure you have the right version of Eclipse Installed
Recommended to use Eclipse Java EE version
Recommended Eclipse Version
- Oxygen https://www.eclipse.org/downloads/packages/release/Oxygen/
- Eclipse Java EE version
Tip : Troubleshooting Embedded Maven in Eclipse
This video is good start for your troubleshoot embedded maven issues in Eclipse - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZZw8XNz5N-c&list=PLBBog2r6uMCSmMVTW_QmDLyASBvovyAO3&index=5
In Windows, use Window -> Preferences for Preferences.
There are typically 4 reasons for errors with Embedded Maven in Eclipse
Error : You are not using a JDK
Failed to execute goal org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-compiler-plugin:3.2:compile (default-compile) on project in28minutes-multi-module-model: Compilation failure [ERROR] No compiler is provided in this environment. Perhaps you are running on a JRE rather than a JDK?
Fix - You would need to configure Eclipse to use JDK instead of JRE
- Go to Your Eclipse > (Window/Eclipse) -> Preferences -> Java -> Installed JRE’s
- Change to use a JDK
Following links will help you if you have questions
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/13635563/setting-jdk-in-eclipse
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/19655184/no-compiler-is-provided-in-this-environment-perhaps-you-are-running-on-a-jre-ra
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/21099072/eclipse-maven-error-no-compiler-is-provided-in-this-environment
Error : You are not connected to internet or You are behind a proxy!
Maven downloads the dependencies (i.e. frameworks and libraries(jars)) from the Maven repository (repo.maven.apache.org).
This is the error you would see
Plugin org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-compiler-plugin:3.1 or one of its dependencies could not be resolved: Failed to read artifact descriptor for org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-compiler-plugin:jar:3.1: Could not transfer artifact org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-compiler-plugin:pom:3.1 from/to central (https://repo.maven.apache.org/maven2): sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target -> [Help 1]
Run this command at command prompt or terminal
telnet repo.maven.apache.org 80
If you are able to connect you should see this.
telnet repo.maven.apache.org 80
Trying 151.101.200.215...
Connected to maven.map.fastly.net.
Escape character is '^]'.
If you do not see above text Connected to maven.map.fastly.net. you would need to check your internet connection.
If you are trying this at work, you might be behind a proxy.
You need to talk to maven experts in your organization to figure out the right settings.
- Here’s a discussion which will be useful
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/25911623/problems-using-maven-and-ssl-behind-proxy
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/5074063/maven-error-failure-to-transfer
- The section below shows how to configure a proxy in Eclipse
Configuring a Proxy
Maven plugin uses a settings file where the configuration can be set. Its path is available in Eclipse at Window -> Preferences -> Maven -> User Settings. If the file doesn’t exist, create it and put on something like the example below:
<settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.0.0.xsd">
<localRepository/>
<interactiveMode/>
<usePluginRegistry/>
<offline/>
<pluginGroups/>
<servers/>
<mirrors/>
<proxies>
<proxy>
<id>myproxy</id>
<active>true</active>
<protocol>http</protocol>
<host>192.168.1.100</host>
<port>6666</port>
<username></username>
<password></password>
<nonProxyHosts>localhost|127.0.0.1</nonProxyHosts>
</proxy>
</proxies>
<profiles/>
<activeProfiles/>
</settings>
Error : Files Downloaded by Maven are Corrupt
Typical Errors
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: ch/qos/logback/classic/turbo/TurboFilter
at java.lang.Class.getDeclaredConstructors0(Native Method)
at java.lang.Class.privateGetDeclaredConstructors(Unknown Source)
at java.lang.Class.getConstructor0(Unknown Source)
Could not find or load main class com.springboot.app.Application
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Failed to read Class-Path attribute from manifest of jar file:/home/edas/.m2/repository/javax/servlet/jstl/1.2/jstl-1.2.jar
And here is my the complete exception stack
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Failed to read Class-Path attribute from manifest of jar file:/C:/Users/pervacio/.m2/repository/org/springframework/security/spring-security-config/5.0.0.M3/spring-security-config-5.0.0.M3.jar
Options that can be tried are listed below:
Force Update of Snapshots/Release
- Right click on your project -> Maven -> Update Project -> Use “Force Update of Snapshots/Releases” -> Check this checkbox
Purge Your Maven Repository
This can be done in two ways
-
Inside Eclipse - Right click on the project > Run as Maven Build > dependency:purge-local-repository
-
From Command Prompt cd to the project of the folder
mvn dependency:purge-local-repository
Delete your local repository
This will be last resort
Error : org.codehaus.plexus.archiver.jar.Manifest.write(java.io.PrintWriter)
Reason - You are using an old version of Eclipse without the latest maven archiver plugin
You get this error
org.codehaus.plexus.archiver.jar.Manifest.write(java.io.PrintWriter)
Recommended Actions
- Recommended - Download latest version of Eclipse
- Other option - It might be a problem with your specific version of eclipse : https://github.com/tesla/m2eclipse-mavenarchiver/issues/9. You can try updating m2e.
- Eclipse > Goto Intall New Software then input https://otto.takari.io/content/sites/m2e.extras/m2eclipse-mavenarchiver/0.17.0/N/LATEST/ and continue.
- Go ahead and install the plugin
For more information read these
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/37936646/eclipse-2-0-2-and-maven-0-17-configuration
- https://github.com/tesla/m2eclipse-mavenarchiver/issues/8
Error : Unsupported major.minor version 52.0
Reason - You are using an old version of JDK
You would get this error
Unsupported major.minor version 52.0
This error happens when you try to run code compiled using JDK 8 in a lesser version of JDK or JRE.
Fix
- If you do not have JDK 8, go ahead an install it.
- Configure Eclipse to use JDK 8. Refer to “You are not using a JDK” section to find out how to configure JDK 8
Tip : Your Project Maven configuration should be configured to compile at Java 8
If you are using Spring Boot, check configuration in Approach 1.
If you are doing a JSP/Servlet or a Spring MVC course without using Spring Boot use Approach 2.
Approach 1 : Spring Boot Project
In pom.xml, the property java.version should be set to 1.8.
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<maven-jar-plugin.version>3.1.1</maven-jar-plugin.version>
</properties>
Approach 2: Non Spring Boot Project
In pom.xml, the source and target of maven-compiler-plugin should be set to 1.8
<project>
[...]
<build>
[...]
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
[...]
</build>
[...]
</project>
Error : On Maven > Update Project, Java 1.4 is auto selected
Ensure that you have the latest version of Eclipse and Java installed.
Error : Changes you made are not reflected
- Did you restart the server?
- Did you stop and start the server?
- Did you reload your web page?
Changes to configuration and web.xml are reflected only when you completely restart the server.
Q : What should I do when some other application is using default port 8080?
Embedded servlet container failed to start. Port 8080 was already in use.
You have two options
- Option 1 - Identify and stop the process that’s listening on port 8080 or
- Option 2 - Configure this application to listen on another port.
Option 1 - Kill
- In Eclipse console tab, on the right hand side, click the double cross icon (Kill all terminated launches). You should see the running program highlighted by a red terminate button. You can kill the red button to kill the running application.
- In windows, Use Ctrl + Shift + Esc to launch windows task manager. Kill all java.exe or javaw.exe
- In Mac, You can use one of these commands to find the PID of process using 8080
netstat -vanp tcp | grep 8080 sudo lsof -i tcp:8080 - After you have the PID, execute the command below:
kill -9 <PID>
Option 2 - Switch Port
Add a property in application.properties
server.port = 8081
java.net.BindException: Address already in use: JVM_Bind <null>:8080.
You have two options
- Option 1 - Identify and stop the process that’s listening on port 8080 or
- Option 2 - Configure this application to listen on another port.
Option 1 - Kill
- In Eclipse console tab, on the right hand side, click the double cross icon (Kill all terminated launches). You should see the running program highlighted by a red terminate button. You can kill the red button to kill the running application.
- In windows, Use Ctrl + Shift + Esc to launch windows task manager. Kill all java.exe or javaw.exe
- In Mac, You can use one of these commands to find the PID of process using 8080
netstat -vanp tcp | grep 8080 sudo lsof -i tcp:8080 - After you have the PID, execute the command below:
kill -9 <PID>
Option 2 - Switch Port
Option 2a - change pom.xml. port is changed to 8081.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<configuration>
<port>8081</port>
</configuration>
</plugin>
Option 2b - Instead of tomcat7:run use the command below to run the application. This will run it on port 8081
-Dmaven.tomcat.port=8081 tomcat7:run
Q : Do I need to install Tomcat seperately for this course?
During the course we would configure a tomcat plugin or embedded tomcat (in Spring Boot courses), which will download tomcat 7 and use it.
You don’t need Tomcat installed on your system.
Q : Why do we use this specific project structure in all our courses?
We follow maven standard project structure.
We recommend you spend sometime understanding this directory layout
- https://maven.apache.org/guides/introduction/introduction-to-the-standard-directory-layout.html.
Q : What software do you use for your diagrams or Mind Maps?
Its called MindMup. https://www.mindmup.com/
I loved the first version of it. And am finding it difficult to adapt to the second version. But as usual, we programmers find a way :)
Q : How to debug the application?
Instead of Run as -> Maven application, use Debug as -> Maven application. Add your breakpoints. You should be all set.
If you are using Spring Boot and Running using Run as -> Java application, then you can use Debug as -> Java Application. Add your breakpoints. You should be all set.
Q : How do I configure auto restarting the server whenever source code changes?
If you are using Spring Boot, check configuration in Approach 1.
If you are doing a JSP/Servlet or a Spring MVC course without using Spring Boot use Approach 2.
Approach 1 : Spring Boot Project
In pom.xml, add a dependency on devtools and restart the server. You are all set.
If you are using Intellij, there is one more configuration you need. Check out the intellij faq section.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
Approach 2: Non Spring Boot Project
Use <contextReloadable>true</contextReloadable> in your pom.xml maven plugin configuration. Restart the server. You are all set.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<configuration>
<path>/</path>
<contextReloadable>true</contextReloadable>
<port>8080</port>
</configuration>
</plugin>
Q : Can I use jboss instead of tomcat server?
Yeah. You can find more details of how to use the jboss maven plugin at https://docs.jboss.org/jbossas/7/plugins/maven/latest/examples/deployment-example.html.
Q : How to get the projects to run in Tomcat 8 or 9?
I’ve done a quick search to find the plugins for tomcat 8 and tomcat 9. Here’s the best I could find
- http://jtuts.com/2016/09/14/run-embedded-tomcat8-maven/
See also here: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/26883836/tomcat-8-maven-plugin-for-java-8
Maven
Q : Why Maven?
You don’t want to store all the libraries in your project!
You want to tell I need A, B, C and you would want the tool to download the libraries and make them available to you.
That’s Maven. The tool which you use to manage the libraries.
If you need a new version of the library, you can change the version and your project is ready!
Also, You don’t need to worry about what libraries your library needs to work. For example, Spring might need other libaries - logging, xml etc.
Once you declare a dependency on Spring, Maven would download
- Spring
- And all dependencies of Spring
Isn’t that cool?
Q : What is ArtifactId and GroupId?
You don’t want to store all the libraries in your project!
So, you define dependencies in your pom.xml.
Maven would download the dependencies and make them available for use in your project.
But, how does Maven know what dependency to download?
You need to tell it by giving the details of the dependency.
Just like you can identify a Java class with a class name and a package name, you can identify a maven artifact by a GroupId and an ArtifactId.
Q : How to know the exact string and name of a dependency and its artifactid?
You can either google or you can visit our Github repository.
You can find it on the home page of the section on github
(Details would have been explained in the introduction video of the section)
- For example - https://github.com/in28minutes/spring-web-services/tree/master/restful-web-services
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-hateoas</artifactId>
</dependency>
Q : What’s the difference between scope and phase?
A scope specifies areas of the application, a dependency can be used. I can use the dependency in tests or I can used it in source code or I can use it when I run the application.
Phase - Different steps in the build life cycle. You compile code first. Then compile test code. Then you run unit tests, Then you run integration tests and so on..
Q : Maven - How did a specific jar end up in our deployable?
In Maven terminology, what you are trying to see is called a dependency tree.
You can type in the command mvn dependency:tree to figure it out.
In eclipse. Right click on Project > Run as > Maven Build > dependency:tree
Q : What is a SNAPSHOT as in 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT?
A project in development uses a snapshot version. Once you have completed developing a version you would release it as 0.0.1 or 0.0.1-RELEASE.
The next version in development will be 0.0.2-SNAPSHOT.
Versioning convention is MAJOR.MINOR.FIX
You can read more about it here : http://books.sonatype.com/mvnref-book/reference/pom-relationships-sect-pom-syntax.html
Q : What is difference between runtime and provided scopes?
Provided is when you expect the runtime environment to provide the dependency. For example, the Java ee api will be provided by tomcat or web sphere. We declare it as provided.
Let’s say you want to use a specific class from a jar in your code. However, you don’t want that jar to be part of your deployable unit. You want this jar to be provided by the runtime server - say tomcat or web sphere or web logic. In those cases, we use a scope of provided to indicate that
- It is NOT included in Deployable unit
- It is available while compiling code
Let’s say We would want a jar to be only available when running the app and not when compiling it. We would use scope of runtime.
- For example - business layer wants to use the api of data layer but not the implementation of data layer. We will make the implementation dependency of data layer as having a scope of runtime.
<dependency>
<groupId>javax</groupId>
<artifactId>javaee-web-api</artifactId>
<version>6.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
Q : How can you always exclude a specific jar using Maven Exclusions?
Maven exclusion is an awesome feature to exclude dependencies that we would not want to be part of our deployable
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
A good example of using dependency exclusion is logging with Spring Boot. Default logging framework is logback. However, if I want to use log4j, I can exclude logback and add log4j.
- You can read about it here : https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/howto-logging.html#howto-configure-log4j-for-logging
However, there is no concept of general exclusion in Maven.
Dependency exclusion is specific to the dependency where it is declared.
You have to exclude a jar in all the dependencies where it is declared as a dependency.
Tip : Example of a multi layered maven project
https://github.com/in28minutes/MavenIn28Minutes/tree/ master/4.web-application-with-maven
Error : java.lang.ClassNotFoundException
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinitionCustomizer
When ever you get this kind of exception. Find out which jar this class belongs to by doing a google - org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinitionCustomizer
In this example I’m missing spring-beans. So, find the right version and add it in. You are all set.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>4.3.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
Q : Why are we not using Gradle?
Gradle is awesome.
If Gradle came before Maven, that is what I would have used for this course :)
Maven has the first mover advantage and has retained it and hence the choice for this course. But, if Gradle become more popular, I would be the first one to switch :)
If you want to create a Spring Boot app with Gradle, this should help you get started - https://spring.io/guides/gs/gradle/
Eclipse
Q : How do I see the list of methods in a class?
Its called outline. Short cut is Ctrl + O.
Q : How do I become more efficient developer?
First Step. Use Keyboard Shortcuts :)
- Eclipse - https://shortcutworld.com/Eclipse/win/Eclipse-Helios_Shortcuts
- Intellij - https://www.jetbrains.com/help/idea/keyboard-shortcuts-you-cannot-miss.html
Q : How do you download source code to Eclipse so that you can see the code for frameworks?
Its easy. Three Options.
- Ctrl + Click on the Class Name and see if the jar is auto downloaded.
- Right click on your project and go to Maven -> Download JavaDoc, you can also select Maven -> Download Sources
- In Eclipse menus, open Window -> Preferences -> Maven and there you check the box with download sources and download javadoc as well.
Intellij and/or Mac
Q : How to install Maven on MAC OS X?
Recommended Reading
- Updating PATH environment variable - https://www.mkyong.com/maven/install-maven-on-mac-osx/
Q : How do I import a Maven project into Intellij?
Here’s a starting guide
- https://www.jetbrains.com/help/idea/2016.1/importing-project-from-maven-model.html
A few tips:
- When importing project, check the option to “Search for projects recursively”
- https://s31.postimg.org/gadu5g7l7/Options.png
- After importing the project, wait for all background tasks to complete - “Resolving Maven dependencies” etc…..
- https://s31.postimg.org/z448g6v6z/Resolving_Dependencies.png
Q : How do I create and run unit tests (JUnit) with Intellij?
Here’s the complete guide
- https://www.jetbrains.com/help/idea/creating-tests.html
This can be another option for setting up a unit test
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/19330832/setting-up-junit-with-intellij-idea
Error : I’m having a problem running jsps with Spring Boot in Intellij. What should I do?
Changed the scope of the embedded Tomcat dependency to required. Hope this helps anyone using IntelliJ.
Q : Why does Hot reload not work with Spring Boot DevTools and Intellij?
Here’s a quick summary of what you have to do
- Settings –> Build-Execution-Deployment –> Compiler –> enable “Make Project Automatically”.
- Press ctrl+shift+A and search for the registry. Enable following configuration
compiler.automake.allow.when.app.running - Restart IntelliJ.
Recommended Reading
- https://dzone.com/articles/spring-boot-application-live-reload-hot-swap-with
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
Spring
Q : What is the need for a Component Scan?
If you understand component scan, you understand Spring.
The first step of defining Spring Beans is by adding the right annotation - @Component or @Service or @Repository.
However, Spring does not know about the bean unless it knows where to search for it. This part of “telling Spring where to search” is called a Component Scan. You define the packages that have to be scanned.
Once you define a Component Scan for a package, Spring would search the package and all its sub packages for components.
Q : How do you define a Component Scan?
Defining a Component Scan
- If you are using Spring Boot, check configuration in Approach 1.
- If you are doing a JSP/Servlet or a Spring MVC course without using Spring Boot use Approach 2.
Approach 1 : Spring Boot Project
Executive Summary
- If your other packages hierarchies are below your main app with the @SpringBootApplication annotation, you’re covered by implicit components scan.
- if the other packages do not reside under the main package, you should manually add them as @ComponentScan
Detailed Example
Consider the class below:
package com.in28minutes.springboot.basics.springbootin10steps;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootIn10StepsApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext =
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootIn10StepsApplication.class, args);
for (String name : applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
@SpringBootApplication is defined on SpringbootIn10StepsApplication class which is package com.in28minutes.springboot.basics.springbootin10steps.
@SpringBootApplication defines an automatic component scan on package com.in28minutes.springboot.basics.springbootin10steps.
You are fine if all your components are defined in the above package or a sub-package.
However, let’s say one of the components is defined in a package com.in28minutes.springboot.somethingelse
In this case, you would need add the new package into component scan.
Two Options
- Define @ComponentScan(“com.in28minutes.springboot”) - This would scan the entire parent tree of com.in28minutes.springboot.
- Or Define two specific Component Scans by using an array.
- @ComponentScan({“com.in28minutes.springboot.basics.springbootin10steps”,”com.in28minutes.springboot.somethingelse”})
Option 1
@ComponentScan(“com.in28minutes.springboot”)
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootIn10StepsApplication {
Option 2
@ComponentScan({"com.in28minutes.springboot.basics.springbootin10steps","com.in28minutes.springboot.somethingelse"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootIn10StepsApplication {
Approach 2: Non Spring Boot Project
In a non Spring Boot Project, we would typically define the component scan explicitly in an XML application context or a Java Application Context.
Java Application Context
Option 1
@ComponentScan(“com.in28minutes)
@Configuration
public class SpringConfiguration {
Option 2
@ComponentScan({"com.in28minutes.package1","com.in28minutes.package2"})
@Configuration
public class SpringConfiguration {
XML Application Context
<context:component-scan base-package="com.in28minutes" />
or Specific Multiple Packages
<context:component-scan base-package="com.in28minutes.package1, com.in28minutes.package2" />
Q : How do I solve Errors related to Component Scan?
Typical errors are shown below:
Error Type 1 :
Server starts up fine but
- My URL is not working
- My login url is not working
- My todo url is not working
Error Type 2
WARNING: No mapping found for HTTP request with URI [/spring-mvc/login] in DispatcherServlet with name 'dispatcher'
WARNING: No mapping found for HTTP request with URI [/login] in DispatcherServlet with name 'dispatcher'
WARNING: No mapping found for HTTP request with URI [/list-todos] in DispatcherServlet with name 'dispatcher'
OR
Error Type 3
No qualifying bean of type [com.in28minutes.springboot.jpa.UserRepository] found for dependency [com.in28minutes.springboot.jpa.UserRepository]: expected at least 1 bean which qualifies as autowire candidate for this dependency. Dependency annotations: {@org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired(required=true)}
Solution
Three possible mistakes a. You have not added the right annotation - @Controller, @Repository or @Controller b. You have not added a component scan. c. The package of your component is not defined in component scan.
You have two options 1) Add the annotation or component scan 2) Move the component to a package already under component scan
Q : What is the difference between @Component and @ComponentScan?
@Component and @ComponentScan are for different purposes.
- @Component indicates that a class might be a candidate for creating a bean. Its like putting a hand up.
- @ComponentScan is searching packages for Components. Trying to find out who all put their hands up.
Q : How do I choose between Spring and CDI?
It’s a choice between
- A framework which popularised DI and IOC (Spring) vs
- A Java EE standard(CDI) that came up as a result of the framework .
I go for the framework, in this case, because it is cutting edge and provides me with more options. There are a lot of guys out there who prefer the standard (CDI) because - well - it is a standard.
The interesting part of the equation is Hibernate vs JPA brings up the same question. However, in Hibernate vs JPA, I prefer JPA.
Summary : There is no choice which is perfect. This is a 55-45 choice. Evaluate what your needs are and make a choice. The good thing is you cannot go wrong with either of the choices.
Q : Why do we write a lot of unit tests in the Spring Master Class course?
Think it this way. Functionally, does Spring allow you to do anything that you were not able to do earlier? The answer is NO. Almost everything that we are doing with Spring today could have been done without Spring 10 years back. So, what does Spring really bring to the table?
Answer is better Design and Testability through Dependency Injection.
To get into the right mindset with Spring, you need to think Testability and Loose Coupling.
Q : What is the use of an @Bean annotation?
Within a Spring Configuration Class , @Bean is used to define beans with custom configuration. You define the beans to be created!
Q : What is the difference between @Bean and @Component?
Here’s a quick fire answer
- @Bean is used in Spring Configuration Files and Classes. It is used to directly instantiate or configure spring beans.
- @Component is used with everything that you want Spring to manage. When Spring sees @Component, it creates a bean for you!
@Component and @Bean do two quite different things, and shouldn’t be confused.
Recommended Reading
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/10604298/spring-component-versus-bean
An Extract
- @Component (and @Service and @Repository) are used to auto-detect and auto-configure beans using classpath scanning. There’s an implicit one-to-one mapping between the annotated class and the bean (i.e. one bean per class). Control of wiring is quite limited with this approach, since it’s purely declarative.
- @Bean is used to explicitly declare a single bean, rather than letting Spring do it automatically as above. It decouples the declaration of the bean from the class definition, and lets you create and configure beans exactly how you choose
Q : What is the difference between @Component, @Service and @Repository annotations?
At the core, all of these define spring beans. However, you can further classify them based on the layer you are using them.
- @Component - Generic Component
- @Repository - encapsulating storage, retrieval, and search behavior typically from a relational database
- @Service - Business Service Facade
- @Controller - Controller in MVC pattern
In addition, these can be used at later point to add additional behaviour using AOP, for example.
- For example, in case of @Repository, Spring automatically wires in JDBC Exception translation features.
By using a specific annotation, you are giving more information to the framework about your intentions.
Q : Can we use @Component annotation instead of @Service for Business Services?
Heres an extract from spring documentation. Since we were creating a business layer service, we used @Service.
“@Component serves as a generic stereotype for any Spring-managed component; whereas, @Repository, @Service, and @Controller serve as specializations of @Component for more specific use cases (e.g., in the persistence, service, and presentation layers, respectively). What this means is that you can annotate your component classes with @Component, but by annotating them with @Repository, @Service, or @Controller instead, your classes are more properly suited for processing by tools or associating with aspects. For example, these stereotype annotations make ideal targets for pointcuts. Of course, it is also possible that @Repository, @Service, and @Controller may carry additional semantics in future releases of the Spring Framework. Thus, if you are making a decision between using @Component or @Service for your service layer, @Service is clearly the better choice. Similarly, as stated above, @Repository is already supported as a marker for automatic exception translation in your persistence layer.”
Q : What is the difference between web.xml and the Spring Context - servlet.xml?
Short Answer:
- web.xml - Java EE Web application Standard. Meta data and configuration of any Java EE compliant web application is stored in web.xml.
- todo-servlet.xml - Spring Configuration file. Specific to Spring Framework.
Long Answer:
web.xml is a default Web Application configuration descriptor, it’s a core part of any WAR (Web application ARchive) and it is not really related to Spring, it’s more like a Web App standard. You usually provide all the servlet related mappings/configuration in this file, then this file is picked up and used by the Web Server (like Tomcat) to set up your application. Again, it has little to do with Spring, you can map any kind of servlet in there not necessarily Springs DispatcherServlet.
todo-servlet.xml is a Spring specific configuration file used to launch up the Application Context. Application Context is the core spring component implementing IoC (Inversion of Control). The xml contains Spring bean declarations, annotation-enabling configuration, etc.
So basically, web.xml defines the servlet and specifies which Spring application context file should be associated with this servlet (you can have different servlets use different app contexts), and the Spring application context defines the concrete configuration for this servlet and it’s environment, e.g. which ViewResolver should it use and with what prefixes/suffixes.
Q : Should we use XML or Annotation based wiring?
Which is better depends on a) context b) preference of the team.
If the configuration is specific to a bean, that is part of the current project code base - for example @Service, @Component, @Autowired - I prefer annotations.
However, when it comes to some application related configuration or a common configuration example @ComponentScan, I do not really have a preference. I would leave it to the team. However, I would definitely want the entire team to discuss and agree what they prefer.
Q : Can we do autowiring with Non Setter and Non Constructor Methods?
Yes you can.
@Autowired annotation can be used with constructor, setter method or just any other method. Whenever Spring finds @Autowired annotation it will try to find beans matching to method parameters and will invoke that method. If multiple methods (setter or non-setter) have @Autowiredannotation, all will be invoked by Spring after bean instantiation.
Whenever you use an @Autowired on a method in the bean, it will be called after bean instantiation. So, this method would be called and Spring would auto wire the matching objects from the Spring Context.
Here’s a recommended reading:
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/30188262/spring-autowired-for-setter-methods-vs-non-setter-methods
Q : Where should we use Checked Exceptions?
I’ve a simple philosophy!
If you can do something about an Exception other than showing an error page to the user, then consider Checked Exceptions. You want the consumer of the method to do something about that exception!
In all other scenarios where there is nothing a programmer can do - other than showing an error page - use Unchecked exceptions.
I love keeping exception handling code to a bare minimum!
That’s what Spring enables by converting most Checked exceptions into Runtime (also called Unchecked) exceptions.
Q : What is the difference between Cross Cutting Concerns and AOP?
A quick fire answer
- Cross Cutting Concerns are features or functionality that you would need in multiple layers - logging, performance management, security etc.
- AOP is one of the preferred approaches to implement Cross Cutting Concerns.
Q : What is difference between IOC and Application Context?
IOC is a concept - Inversion of Control. Instead of the programmer injecting dependencies, the framework takes the responsibility of auto wiring.
ApplicationContext is the Spring implementation of IOC.
Bean Factory is the basic version of IOC Container.
Application Context adds in all the features that are typically needed by enterprise applications.
Q : What is the difference between classPathXmlApplicationContext and annotationConfigApplicationContext ?
- classPathXmlApplicationContext > You want to load an application context using an Spring Config XML present in the class path.
- annotationConfigApplicationContext > You want to load an application context using a Java Config class.
Q : When @Around aspect is introduced the value returned by@AfterReturning is lost. Why is this happening?
The around method should return an Object - value returned by joinpoint.proceed().
@Around("com.in28minutes.spring.aop.springaop.aspect.CommonJoinPointConfig.trackTimeAnnotation()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object retVal = joinPoint.proceed();
long timeTaken = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Time taken by {} is equal to {}",joinPoint, timeTaken);
return retVal;
}
Q : How do you use which autowiring type to use - @Primary or @Qualifier?
If there is a default bean (a bean you prefer over all others) that you want to use most of the times, then go for @Primary and use @Qualifier for non-default scenarios.
If all of the beans have same priority, we would go with @Qualifier always.
If you want to select a bean at runtime, thats business logic - Not auto wiring.
You would need to create a separate class for Selector which has both the sorting algorithms auto wired. It should have the business logic to choose the appropriate algorithm.
Q : What are the New Features in Spring Framework 5.0?
I’ve recently wrote a book on Mastering Spring 5.0.
Important features in Spring 5.0 are Functional Web Framework, Kotlin and Reactive Programming support. But none of these are mainstream yet.
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/wiki/What%27s-New-in-the-Spring-Framework#whats-new-in-spring-framework-5x
Q : What are the possible reasons of preDestroy not being called?
- Replace ApplicationContext with ConfigurableApplicationContext and call applicationContext.close() at the end.
Q : Compare Application Context vs IOC Container vs Web Container vs EJB Container
Do we need a Web Container to run a Spring Boot Application?
Basically spring runs anywhere where we have a JVM because that JVM will have capability to run some sort of a container or capability to run an application. Difference would be that the mechanism to load application context would be different based on where it runs. e.g. 2 high level categories - ApplicationContext for Web and Applicationcontext for standalone and again in those 2 categories we will choose “how” and “from where” we want to load that metadata for those applicationContext.
Web Container & EJB Containers are part of the application/web servers - Tomcat, Websphere, Weblogic. They run what ever application is given to them. Java EE defines a contract for web applications (web.xml etc etc) and these are the implementations of that contract.
Spring Container is part of the application you are building - the jar or the war. It can run inside a web container, EJB container or even without them :) You can launch it as a java application or you can even run it in an embedded server.
Notes : Notes from Rodolfo
Link to this file: https://s3.amazonaws.com/espanol-libros/AllLinks.rtf
Spring Master Class:
https://s3.amazonaws.com/espanol-libros/Spring/Section+03+Eclipse+in+5+Steps.rtf
https://s3.amazonaws.com/espanol-libros/Spring/Section+04+Maven+in+5+Steps.rtf
https://s3.amazonaws.com/espanol-libros/Spring/Section+09+Basic+Web+Application.rtf
https://s3.amazonaws.com/espanol-libros/Spring/Section+12+Databases.rtf
Q : How do we inject different bean depending on the configuration in application.properties?
Consider the example
interface GreetingService {
public String sayHello();
}
Two components
@Component(value="real")
class RealGreetingService implements GreetingService {
public String sayHello() {
return "I'm real";
}
}
@Component(value="mock")
class MockGreetingService implements GreetingService {
public String sayHello() {
return "I'm mock";
}
}
application.properties
application.greeting: real
Adding @Resource with the name of the property
@RestController
public class WelcomeController {
@Resource(name="${application.greeting}")
private GreeterService service1;
Error : Log4j problems with Spring 5!
- TODO
Q : What is the minimum baseline Java Version for Spring Boot 2 and Spring 5?
Spring 5.0 and Spring Boot 2.0 requires Java 8 or later. Java 6 and 7 are no longer supported.
Recommended Reading
- https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/wiki/Spring-Boot-2.0.0-M1-Release-Notes
Error : Getting SLF4J errors and not getting logger output in Step 19?
SLF4J: Failed to load class "org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder".
SLF4J: Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation
SLF4J: See http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#StaticLoggerBinder for further details.
As we start removing Spring Boot and bringing in Spring core,in Step 19 of Spring In Depth Section, you would see
- A few SLF4J errors
- Logging does not work
Do not worry about them. We will fix them in the next step Step 20 by adding logback as the logging framework.
Error : No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath
It usually happens when you are having conflicts in Java and Spring versions.
- Please refer http://stackoverflow.com/questions/22938689/info-no-spring-webapplicationinitializer-types-detected-on-classpath.
JSP Servlets and Spring MVC
Q : What is the difference between @Controller and @RestController?
@RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody
The response from the @RestController are directly returned as a response after conversion to JSON or XML.
In Summary
- @Controller : Uses a view resolver to find the view. You are returning either the View, View Name or Model and View.
- @RestController : You are returning a bean. The bean would be converted to a JSON using a Jackson message converter.
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public class MyController { }
@RestController
public class MyRestController { }
Q : Why is there no context root in the request url for each web application?
Great question. The magic is in path configuration of tomcat7 maven plugin. We use / as the path. Therefore, there is no need for a context root. You can configure a path of your choice and that becomes the context root for your web app.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<configuration>
<path>/</path>
<contextReloadable>true</contextReloadable>
</configuration>
</plugin>
Q : What does tomcat7:run exactly mean?
We use a maven plugin for integrating with tomcat7. The plugin would take care of downloading tomcat and installing the war in it.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<configuration>
<path>/</path>
<contextReloadable>true</contextReloadable>
</configuration>
</plugin>
You can find more documentation here
- http://tomcat.apache.org/maven-plugin-trunk/tomcat7-maven-plugin/plugin-info.html
You can read more down here as well
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/7823346/mvn-tomcat7run-how-does-it-work
- http://tomcat.apache.org/maven-plugin-trunk/tomcat7-maven-plugin/run-mojo.html
Q : How is the URL decided with Spring MVC?
First things are the port and the context root. We use the default port - 8080 and we set path to /. So, the initial url is http://localhost:8080.
pom.xml
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<configuration>
<path>/</path>
<contextReloadable>true</contextReloadable>
</configuration>
</plugin>
We configured dispatcher servlet with a url-pattern /. So, it handles all request to http://localhost:8080
web.xml
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/todo-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
The showWelcomePage method is mapped with a path of “/”. So, a request to http://localhost:8080 will be handled by this method.
@Controller
public class WelcomeController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String showWelcomePage(ModelMap model) {
model.put("name", getLoggedInUserName());
return "welcome";
}
TodoController showTodosList method is used to display the list of todos. The uri configured is /list-todos. So, it handles requests to http://localhost:8080/list-todos.
@Controller
public class TodoController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/list-todos", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String showTodosList(ModelMap model) {
String user = getLoggedInUserName();
model.addAttribute("todos", service.retrieveTodos(user));
return "list-todos";
}
Error : No plugin found for prefix ‘tomcat7’ in the current project
No plugin found for prefix ‘tomcat7’ in the current project and in the plugin groups [org.apache.maven.plugins, org.codehaus.mojo] when trying to run the application using run with Maven tomcat7:run
First thing I would check is if maven plugin configured in your pom.xml as mentioned in https://github.com/in28minutes/SpringMvcStepByStep/blob/master/Step01.md
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<configuration>
<path>/</path>
<contextReloadable>true</contextReloadable>
</configuration>
</plugin>
If it is configured correctly then I would check these two links if they are of any use
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/24311383/maven-no-plugin-found-for-prefix-tomcat7-in-the-current-project-and-in-the-p
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/21073123/maven-no-plugin-found-for-prefix-tomcat7-in-the-current-project
Q : Is this kind of Tomcat server usage what is commonly referred to as “Embedded Tomcat Server” ?
This answer applies only to our Basic JSP Servlets and Spring MVC Courses. For all the courses using Spring Boot we use an embedded tomcat server.
Think about what you would need to be able to deploy your application (typically) on a virtual machine.
- Step 1 : Install Java
- Step 2 : Install the Web/Application Server (Tomcat/Websphere/Weblogic etc)
- Step 3 : Deploy the application war
What if we want to simplify this?
How about making the server a part of the application?
You would just need a virtual machine with Java installed and you would be able to directly deploy the application on the virtual machine. Isn’t it cool?
This idea is the genesis for Embedded Servers.
When we create an application deployable, we would embed the server (for example, tomcat) inside the deployable.
For example, for a Spring Boot Application, you can generate an application jar which contains Embedded Tomcat. You can run a web application as a normal Java application!
Embedded server is when our deployable unit contains the binaries for the server (example, tomcat.jar).
Basic Spring MVC and JSP Servlet courses do not use embedded servers
In our basic Spring MVC and JSP Servlet courses, we use the age old approach of generating wars. However, we use a tomcat maven plugin to simplify deployment.
The plugin will take care of downloading Tomcat and deploying the war to it. One less thing for you to worry about.
However, this is not really an embedded server. This is midway between an external server and an embedded server.
All our Spring Boot courses use Embedded Servers
All our Spring Boot courses use embedded Tomcat server.
Q : How do we handle errors to non existing URL Paths with Spring MVC?
You can add an error page for 404 in your web.xml.
<error-page>
<error-code>404</error-code>
<location>/error404.jsp</location>
</error-page>
Q : How do we configure a welcome page?
Let’s say your Login Controller is mapped to login.do and you would want that to be default page to be rendered when you type in http://localhost:8080.
This can be achieved by having a welcome file list configured in the web.xml.
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>login.do</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
Q : Why do we teach JSP and Servlets in the first section of Spring MVC Course?
I would recommend you to read “The in28Minutes Way” - https://github.com/in28minutes/in28minutes-initiatives/tree/master/The-in28Minutes-Way#we-want-you-to-be-strong-on-the-fundamentals
We think that understanding the fundametals of a tool, framework or a language is what makes you an expert. While you want to quickly learn how to use a framework, the key difference between an expert and a novice is “How deep do you understand the framework?”.
In Spring MVC course, we teach you basics of JSPs and Servlets and then move to Spring MVC to ensure you understand why we are using Spring MVC.
Q : Why do we use @ResponseBody sometimes and ResponseEntity some other times?
Quick Answer - You use ResponseEntity when you want to customize the Response Status. In all other situations, we use @ResponseBody.
Example 1
@GetMapping(value=”/resource”) @ResponseBody public Resource sayHello() { return resource; }
Example 2
@PostMapping(value=”/resource”)
public ResponseEntity
There are a variety of HTTP Response Status Codes that you can return with your response.
- 200 - SUCCESS
- 201 - CREATED
- 404 - RESOURCE NOT FOUND
- 400 - BAD REQUEST
- 401 - UNAUTHORIZED
- 500 - SERVER ERROR
With @ResponseBody the only response type that goes out is SUCCESS (Example 1). (or 500 if a server error happens)
Let’s say you are creating a resource. You would want to send a status of 201 CREATED. In this case, we use ResponseEntity as in Example 2.
Q : What is difference between Spring 5 and Spring 4 in terms of developing web application in the course? Does it matter if a new version is used ?
There will be one problem you will face when you use Spring 5.
When you get to /src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/views/todo.jsp - You should use modelAttribute instead of commandName
Instead of
<form:form method="post" commandName="todo">
Use
<form:form method="post" modelAttribute="todo">
You can read more about this here :
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/21495616/difference-between-modelattribute-and-commandname-atributes-in-form-tag-in-sprin
Q : What is the difference between Filters, Listeners and Interceptors?
Conceptually similar. Servlet filters can intercept only HTTPServlets. Listeners can intercept a few specific events. How do you intercept events which are neither of the above.
Both filters and interceptors do the same things - They intercept something and do something before/after an action is performed.
Java EE uses the term filter (in web.xml) and Spring calls them Interceptors.
Thats where AOP comes in. You can intercept calls to any object with AOP.
More Reading
- http://www.programering.com/a/MzM3EDNwATY.html
Q : What is the difference between ModelMap and ModelAndView?
Model is an interface while ModelMap is a class.
ModelAndView is just a container for both a ModelMap and a View object. It allows a controller to return both as a single value.
I usually like ModelAndView to return the model and view from a controller. However, there is an option where you can just add values to ModelMap and return viewname from the controller method.
More Reading
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/16951609/when-to-use-modelandview-vs-model-in-spring
Q : What is the difference between model.put() and model.addAttribute()?
Code for addAttribute method is listed below. It does an additional null check before calling a put. Doesn’t really matter which one you use.
I like addAttribute because you are separated from underlying data structure (put implies you are using a hashmap).
/**
* Add the supplied attribute under the supplied name.
* @param attributeName the name of the model attribute (never null)
* @param attributeValue the model attribute value (can be null)
*/
public ModelMap addAttribute(String attributeName, Object attributeValue) {
Assert.notNull(attributeName, “Model attribute name must not be null”);
put(attributeName, attributeValue);
return this;
}
One more difference is that addAttribute returns the ModelMap back. So, you can chain calls.
model.addAttribute(“attribute1”,”value1”).addAttribute(“attribute2”,”value2”);
Q : How do you pass values from Java Controller to JSP?
This is done through Model. You put a value in the model object in your Controller. Spring MVC makes it available to the JSP.
Put a list with name “todos” in the model. Spring MVC makes it available with name “todos” in the JSP.
We can access the value in the JSP using ${todos}
<c:forEach items ="${todos}" var= "todo"> - In this forEach var=”todo” declares a variable todo.
You can think of it similar to Java Enhanced for loop - “for(Todo todo:todos)” ).
Q : What is Form Binding?
We want to take values from screen and store them to the database. The value on the HTML form needs to be transferred to the bean on the Controller.
If you use the Spring MVC form tags, Spring MVC automatically takes care of the binding the values in the HTML form to the bean.
- I would recommend you to do a View Source on the browser and see the html that is generated with the form tags
You need a form to bind the value to a bean.
You can look up the documentation for Spring MVC Form Tags for more details.
I would recommend you to start looking at each of the things thats happening in the browser. See the html that is generated (view source), look at what are the values in the request when you click the submit button on the screen (Look at the network tab : http://code.tutsplus.com/articles/chrome-dev-tools-networking-and-the-console–net-28167)
Couple of Sources which might be useful for you
- Spring MVC Documentation : http://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/htmlsingle/#mvc
- Spring MVC Code : https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/tree/master/spring-webmvc/src
Q : What is WEB-INF exactly? Why so we need it?
From the specification, “A special directory exists within the application hierarchy named WEB-INF. This directory contains all things related to the application that aren’t in the document root of the application. The WEB-INF node is not part of the public document tree of the application. No file contained in the WEB-INF directory may be served directly to a client by the container. However, the contents of the WEB-INF directory are visible to servlet code using the getResource and getResourceAsStream method calls on the ServletContext, and may be exposed using the RequestDispatcher calls.”
More Reading
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/19786142/what-is-web-inf-used-for-in-a-java-ee-web-application
Q : Why do we use Hibernate Validator?
Hibernate Validator is not related to Database. It is a validation framework.
Hibernate Validator 5.x is the reference implementation Bean Validation 1.1!
Actually, you can use any implementation of Bean Validation API. However, there are really no other popular options.
As you can see at http://beanvalidation.org/2.0/, Hibernate Validator is the only one which is certified!
Q : Are Model objects specific to a request?
Yes. They are specific to a request.
Model objects cannot be shared across requests. So, 2 different requests mean 2 different model objects.
If you look at the jsp for a todo page, it shares the responsibility of creating a new todo and modifying an existing todo. And the todo object is binded to the form.
To display todo page for new todo, we need a model with no values. That’s the first model object that’s created.
- This is used only for the display of new todo page.
Once the page is displayed, the first model does not exist anymore.
When user fills in the values and clicks submit, the values in the form gets bound to a new model object - the second one.
Q : The groupid for jstl jar is jstl and not javax.servlet
Yeah. There seems to be some confusion around this. As I understand java.servlet is recommended.
Recommended Reading
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2276083/include-jstl-dependency-with-maven
Its not a recommendation I give often, but feel free to use whatever works in this specific scenario
Q : Why are we using request GET method for “delete-todo” request?
Question Continued - Shouldn’t we be using DELETE request method?
The data we use to execute the DELETE is just an id. It is not sensitive information. We can add a check to see if the user has permission on the id to execute a delete before executing a delete. Changing it to POST does not give us any added advantages.
However, when we create RESTful services, we should use DELETE.
Q : Why do we need xmlns hyperlinks? like http://www.springframework.org/schema/bean
These are generic and would work with all version of Spring Framework. Otherwise we would need to change the version every time we upgrade Spring Framework.
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/11610790/what-difference-does-an-xmlns-definition-make-in-a-spring-configuration-file
Error : View is not resolving to a JSP
In your web.xml, ensure your url-pattern is set to /spring-mvc/
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/spring-mvc/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
If you have /* dispatcher servlet would handle requests to the views as well. We don’t want that!
Q : How to use own CSS with Spring MVC?
Spring Configuration XML
JSP
Q : Where should we place our static (css, js, html) resources in a Spring MVC application?
For the Java script, I would have separate java script files and include them into your jsp.
Here’s a small discussion where static files should be located:
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/7836930/where-do-css-and-javascript-files-go-in-a-maven-web-app-project
Q : How to add a custom login page in Spring Security?
Complete example down here
- http://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/current/guides/html5/form-javaconfig.html
Other Recommended Reading
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/3.2.0.RELEASE/guides/form.html
- http://www.concretepage.com/spring-4/spring-4-mvc-security-custom-login-form-and-logout-example-with-csrf-protection-using-annotation-and-xml-configuration
Q : How can you authenticate by connecting to a database with Spring Security?
Complete example down here :
- https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/tree/master/spring-boot-samples/spring-boot-sample-web-secure-jdbc
Q : Why is request method POST recommended compared to GET for sensitive data?
Following are the steps that happen when you interact with a web page
- Browser : You enter the details
- Browser : Creates a POST request where details are put into the request (and encrypted if you are using https)
- Routers and Network : The POST request is sent through multiple routers before it reaches the destination
In the case of a get request and post request, in steps a and b you can see the details on the browser. The real change is in step c.
Important Question to ask is “What is going across the network?”
In the case of GET request, your details are part of url and all routers can see those details. However, in the case of POST, the details are sent as part of the body of the request and hence more safe.
Q : We use ${todo.done} in JSP even though the name of the field in Todo.java is isDone. Shouldn’t we be using ${todo.isDone}?
Isn’t it tricky? Welcome to the fun of Java Beans.
You can try renaming the variable to done or what ever you want. The important thing is what is the name of getters and setters.
Java Beans work based on the names of your getters and setters. The setter is named setDone. So, we use ${todo.done}.
I would recommend playing with getters and setters to understand this further.
public boolean isDone() {
return isDone;
}
public void setDone(boolean isDone) {
this.isDone = isDone;
}
Error : After adding security dependencies - java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AutoProxyUtils.determineTargetClass
HTTP Status 500 - Servlet.init() for servlet dispatcher threw exception
java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AutoProxyUtils.determineTargetClass(Lorg/springframework/beans/factory/config/ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/Class;
at org.springframework.context.event.EventListenerMethodProcessor.afterSingletonsInstantiated(EventListenerMethodProcessor.java:78)
Its a compatibility issue between Hibernate Validator and Spring.
Solution - Change your 4.2.3.RELEASE dependency to 4.2.2.RELEASE and change Hibernate version 5.0.4.Final to 5.0.2.Final
Recommended Reading
- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/34053170/spring-4-2-3-release-and-hibernate-5-0-4-final-compatibility-issue
Q : How do I ensure that session attributes are not part of the request url?
When we use model.put(“name”, name) and name is a session attribute, these parameters are shown in redirected page as parameters in url.
To avoid this, we can use flash attributes.
An example below:
@RequestMapping(value="/Login",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ModelAndView loginValidate(HttpServletRequest req, RedirectAttributes redir){
...
modelAndView.setViewName("redirect:welcome");
redir.addFlashAttribute("USERNAME",uname);
return modelAndView;
}
Error : Spring Security - java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/springframework/web/cors/CorsConfigurationSource
Typically this happens because the schemas in your application context xml are referring to a different Spring Version
Example : You use Spring 5 and your schema’s are referring to Spring 4.0
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
Solving the error - Recommendation is to use generic schema definitions.
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
Error : Unable to find setter method for attribute commandName
org.apache.jasper.JasperException: /WEB-INF/jsp/todo.jsp (line: [12], column: [1]) Unable to find setter method for attribute: [commandName]
commandName is deprecated and is replaced with modelAttribute.
All you have to do is modify the form line within todo.jsp (getting rid of commandName=”todo”), as follows:
<form:form method="post" modelAttribute="todo">
This is further explained in the last step of Spring Boot course in section “Connecting to JPA” - Step 33: Upgrading to Spring Boot 2 and Spring 5
Q : Can I have multiple parameters with the same name in a request?
Let’s take an example
http://localhost:8080/login?name=Ranga&name=Ravi&name=Sathish
You can accept all values using an array in the controller method.
Here’s a snippet!
public String method(@RequestParam(value="name") String[] names){
//if length of names is not 1, throw an error!
//Continue processing.
}
Error : java.lang.IllegalStateException: Neither BindingResult nor plain target object for bean name ‘todo’ available as request attribute
This is a problem with using ToDo as the bean class name instead of Todo.
result.hasErrors()
when I try to add less than 6 chars, error occurs which says:
java.lang.IllegalStateException: Neither BindingResult nor plain target object for bean name 'todo' available as request attribute
2 Possible Solutions
- Rename your ToDo.java to Todo.java (OR)
- Change your method signature to include @ModelAttribute
public String addTodo(ModelMap model, @ModelAttribute(“toDo”) @Valid ToDo todo, BindingResult result) {
Spring MVC makes assumptions about your beans. If your class is ToDo, it expects the name of the object to be toDo. since, we are using todo as the name we need to add in a ModelAttribute annotation.
Error : Request processing failed; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.BeanInstantiationException: Failed to instantiate [com.in28minutes.Todo.Todo]: No default constructor found; nested exception is java.lang.NoSuchMethodException: com.in28minutes.Todo.Todo.()
No default constructor found;
You would need a default constructor
public void Todo() {}
Error : Caused by: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: The servlets named [com.in28minutes.LoginServlet] and [webapp.LoginServlet] are both mapped to the url-pattern [/login.do] which is not permitted
Problem is because there are two servlets with same url pattern.
To fix it, you can delete one of the LoginServlet classes.
Q : How is server picking up index.html and index.jsp even when they are not configured in web.xml?
These are present in the default web.xml present on the tomcat server. Thats why even when you don’t provide a web.xml , these are picked up.
Q : What is the benefit of using view resolver?
Question Continued - Will it not take more time to process a request.
It all boils down to good design!
Do one thing very well.
View Resolver maps a logical view name to a physical view (JSP).
As far as Java is concerned, more method calls does not mean bad performance.
Why am I not able to see todo’s list on screen?
Make sure you use the right user name in the code to retrieve the list of todos.
model.put("todos", service.retrieveTodos("in28Minutes"));
Q : What is @ControllerAdvice?
@ControllerAdvice is common to all the controllers.
All logic that is common to all the controllers is implemented in Controller Advice classes.
Exception handling etc.
Q : What Request method should be used for updating user details?
You would need to use a PUT method for updating a user. You can use a @PutMapping.
Q : What is the difference between put and patch request methods?
- PUT : When you update the entire resource - when you want to update all/most of the fields of a resource.
- PATCH: When you want to update specific details of the resource. All other details remain unchanged.
Spring Boot
Spring Boot is the best Java framework for microservices We recommend you to become an expert at Spring Boot!
Q : What should be the first things I read about Spring Boot?
Here are a list of articles for you to get started with understanding Spring Boot.
- Spring Boot vs Spring vs Spring MVC
- Basics of Spring Boot - Auto Configuration, Spring Boot Starter Projects, Spring Boot Starter Parent, Spring Boot Initializr
- Rest Services - Basic Rest Service with Spring Boot, Unit Testing, Integration Testing
- Web Application - Create Basic Web Application with Spring Boot
- Spring Boot Starter Security - Secure Your Rest Services with Spring Boot
What is the minimum baseline Java Version for Spring Boot 2 and Spring 5?
Spring Boot 2.0 requires Java 8 or later. Java 6 and 7 are no longer supported.
Recommended Reading
- https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/wiki/Spring-Boot-2.0.0-M1-Release-Notes
Q : Is Spring Initializr the only way to create Spring Boot Projects?
No.
Spring Initializr makes it easy to create Spring Boot Projects. But you can setup a maven project and add the right dependencies to start off.
In our Spring course, we use 2 approaches to create projects.
- The first one is start.spring.io.
- The other one - setting up a project manually is used in the Section titled - “Basic Web Application”
Setting up a maven project manually
Here are the important steps:
- In Eclipse, Use File -> New Maven Project to create a new project.
- Add dependencies.
- Add the maven plugins!
- Add the Spring Boot Application class
You are ready to go!
Q : Why am I not seeing code completion when updating application.properties in Eclipse?
You would need to install the Spring Eclipse plugin.
- https://marketplace.eclipse.org/content/spring-ide#group-external-install-button
Q : Why do we need spring-boot-maven-plugin?
spring-boot-maven-plugin provides a few commands which enable you to package the code as a jar or run the application
- spring-boot:run runs your Spring Boot application.
- spring-boot:repackage repackages your jar/war to be executable.
- spring-boot:start and spring-boot:stop to manage the lifecycle of your Spring Boot application (i.e. for integration tests).
- spring-boot:build-info generates build information that can be used by the Actuator.
Q : Devtools helps me to restart the server automatically. But, I have a problem. The browser page is not auto refreshed.
Devtool helps the server pick up the change automatically. However, you have to refresh the page manually to execute a new request.
If you would want to auto load the page as well, you can look at LiveReload
- http://www.logicbig.com/tutorials/spring-framework/spring-boot/boot-live-reload/.
In my trials, we found LiveReload buggy. Do let us know if you have a better experience with it.
Q : What and Why Embedded Servers?
Think about what you would need to be able to deploy your application (typically) on a virtual machine.
- Step 1 : Install Java
- Step 2 : Install the Web/Application Server (Tomcat/Websphere/Weblogic etc)
- Step 3 : Deploy the application war
What if we want to simplify this?
How about making the server a part of the application?
You would just need a virtual machine with Java installed and you would be able to directly deploy the application on the virtual machine. Isn’t it cool?
This idea is the genesis for Embedded Servers.
When we create an application deployable, we would embed the server (for example, tomcat) inside the deployable.
For example, for a Spring Boot Application, you can generate an application jar which contains Embedded Tomcat. You can run a web application as a normal Java application!
Embedded server is when our deployable unit contains the binaries for the server (example, tomcat.jar).
Q : How can I add custom JS code with Spring Boot?
Create a folder called static under resources folder. You can put your static content in that folder.
For your example the path to myapp.js would be resources\static\js\myapp.js
You can refer to it in jsp using
<script src="/js/myapp.js"></script>
Error : HAL browser gives me unauthorized error - Full authentication is required to access this resource.
{
"timestamp": 1488656019562,
"status": 401,
"error": "Unauthorized",
"message": "Full authentication is required to access this resource.",
"path": "/beans"
}
Two options
Option 1 : Disable security
application.properties
management.security.enabled: FALSE
Option 2 : Search for password in the log and pass it in the request header
Error : Hal Browser and Spring Boot Actuator are not working
Question Continued - You can only get a json response. /application, /application/status and /application/info
With 2.0.0.M4 Spring Boot is making a lot of changes to Actuator.
Do not use SNAPSHOT versions
For now we recommend using 2.3.1.RELEASE with all courses. I will wait for the changes that are introduced with M4 to stabilize before incorporating into the course.
Recommmended Reading
- https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/wiki/Spring-Boot-2.0.0-M4-Release-Notes
Solution : Update your pom.xml
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
If you are using Milestone (M1, M2, M3…) or SNAPSHOT version you need this configuration
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
Q : How does path=”users”, collectionResourceRel=”users” work with Spring Data Rest?
@RepositoryRestResource(collectionResourceRel = "users", path = "users")
public interface UserRestRepository extends
PagingAndSortingRepository<User, Long>
- path - The path segment under which this resource is to be exported.
- collectionResourceRel - The rel value to use when generating links to the collection resource. This is used when generating HATEOAS links.
Q : What is importance of {id} in ServletUriComponentsBuilder.fromCurrentRequest().path(“/{id}”).buildAndExpand(returnQuestion.getId()).toUri();
The name of the variable in the path does not really matter.
You can read more about UriComponentsBuilder here : http://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/javadoc-api/org/springframework/web/util/UriComponentsBuilder
Error : java.lang.ClassCastException: org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationReadyEvent cannot be cast
s.c.e.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster : Non-matching event type for listener: org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer$$Lambda$69/128359175@5e82df6a
java.lang.ClassCastException: org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationReadyEvent cannot be cast to org.springframework.boot.web.context.WebServerInitializedEvent
org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationReadyEvent cannot be cast to org.springframework.boot.web.context.WebServerInitializedEvent
ApplicationReadyEvent is sub-class of SpringApplicationEvent. So, it cannot be type casted to WebServerInitializedEvent.
The code which is triggering the exception is below
try {
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
String msg = ex.getMessage();
if (msg == null || msg.startsWith(event.getClass().getName())) {
// Possibly a lambda-defined listener which we could not resolve the generic event type for
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex);
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
As you can see the exception is being suppressed based on the exception message. I guess this is a scenario which the developer expected.
I could not figure anything more about this code other than the fact that this event is trigged when application is ready to accept requests.
“Event published as late as conceivably possible to indicate that the application is ready to service requests. The source of the event is the {@link SpringApplication} itself, but beware of modifying its internal state since all initialization steps will have been completed by then.”
I dont expect this to cause a problem. Especially because this is logged at debug level.
Q : What is difference between Spring 5 and Spring 4 in terms of developing web application in the course? Does it matter if a new version is used ?
There will be one problem you will face when you use Spring 5.
When you get to /src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/views/todo.jsp - You should use modelAttribute instead of commandName
Instead of
<form:form method="post" commandName="todo">
Use
<form:form method="post" modelAttribute="todo">
You can read more about this here :
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/21495616/difference-between-modelattribute-and-commandname-atributes-in-form-tag-in-sprin
Q : Why am I seeing an extra dialogue asking me to “Select Java Application Type” when I launch a Spring Boot Application?
The best way to run is to right click on the Java Class File you want to run (SpringBootTutorialApplication) > Run As > Java Application.
When you do it on a project, Eclipse finds all the java classes with main methods and asks you to choose among them
Q : What happens in the background when a Spring Boot Application is “Run as Java Application”?
If you are using Eclipse IDE, Eclipse maven plugin ensures that as soon as you add a dependency or make a change to the class file, it is compiled and ready in the target folder! And after that its just like any other Java application.
When you launch the java application, then the spring boot auto configuration magic kicks in.
- It launches up tomcat when it sees that you are developing a web application!
Q : Can we use jetty instead of tomcat in spring-boot-starter-web?
Remove the existing dependency on spring-boot-starter-web and add these in.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>
Error : Failure to transfer org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-parent:pom:2.3.1.RELEASE from https://repo.spring.io/snapshot
SNAPSHOT versions are versions under development. Of late, there are a few issues with some of the SNAPSHOT version of Spring Boot 2. We recommend using 2.3.1.RELEASE for now.
In you pom.xml, you can change the version in the parent as shown below:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
If you are using Milestone (M1, M2, M3…) or SNAPSHOT version you need this configuration
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
Q : Why do we configure Spring Snapshot and milestone repositories?
If you are using Milestone (M1, M2, M3…) or SNAPSHOT version you need this configuration
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
Error : java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Sources must not be empty
Make sure you are running the right Java class. Go to your class containing @SpringBootApplication and right click > Run as Java Application.
In the example below SpringbootIn10StepsApplication has the @SpringBootApplication annotation. So, it is the one you should run as Java Application.
package com.in28minutes.springboot.basics.springbootin10steps;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootIn10StepsApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext =
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootIn10StepsApplication.class, args);
for (String name : applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
Q : Can i use spring boot dev tools for a non spring boot project?
I would recommend you to try JRebel.
Q : What is the difference between Static and Dynamic filtering?
Imagine the same bean being used in two different RESTful services. And these two services want to send out different set of fields in the response.
If we add the @JsonIgnoreProperties annotation on the bean, then we cannot have different set of fields in the responses. Thats why this is called static filtering.
However with dynamic filtering, shown below, you can create two request methods, each having different attributes being sent.
SimpleBeanPropertyFilter filter = SimpleBeanPropertyFilter.filterOutAllExcept("field1", "field2");
FilterProvider filters = new SimpleFilterProvider().addFilter("SomeBeanFilter", filter);
MappingJacksonValue mapping = new MappingJacksonValue(someBean);
mapping.setFilters(filters);
return mapping;
Error : No message found under code ‘good.morning.message’ for locale ‘us’.
Ensure that the name of ResourceBundleMessageSource is the same in both the files related to internationalization.
- In the examples below, we use messageSource as the @Autowired bean name and the @Bean method name.
@Autowired
private MessageSource messageSource;
@Bean
public ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource() {
ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
messageSource.setBasename("messages");
return messageSource;
}
Q : How to generate a WAR file with Spring Boot?
Recommended Reading
- https://spring.io/guides/gs/convert-jar-to-war/
Here’s the direct link to spring documentation
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/htmlsingle/#build-tool-plugins-maven-packaging
Q : How to deploy to a different server with with Spring Boot?
You would need to do 2 Steps
- Generate a war from the project.
- Deploy it to your favourite server (Websphere or Weblogic or Tomcat or …).
Step 1 : This getting started guide should help - https://spring.io/guides/gs/convert-jar-to-war/
Step 2 : Depends on your server
Q : What is the difference between RequestMapping and GetMapping?
- RequestMapping is generic - you can use with GET, POST, PUT or any of the other request methods using the method attribute on the annotation.
- GetMapping is specific to GET request method. It’s just an extension of RequestMapping to improve clarity.
Q : Why do we recommend not to use Spring Data Rest in real world applications?
We think Spring Data Rest is Good for quick prototyping! Be cautious about using this in Big applications!
With Spring Data REST you are exposing your database entitities directly as REST Services.
When you design RESTful services, Best design practices suggests that your interface should consider two important things
- Your Domain Model
- Your Consumers
With Spring Data REST, you are not considering either of those. You just expose entities as REST Services.
Thats why we suggest to use it for quick prototyping or the initial evolution of a project. It may not be a great idea for a fully evolved project.
Q : How do I change the package name of a project in Spring Initializer?
Good news is you can customise it. Click the link “Switch to the full version.“. You would be able to configure the package name you would want!
Q : Where can I find the complete list of properties that can be configured in application.properties?
Here’s the complete guide
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/common-application-properties.html
Hibernate, JPA and In-memory Database
Q : What is the difference between JPA and Hibernate?
Short Story
- JPA is a specification/Interface
- Hibernate is one of JPA implementations
When we use JPA, we use the annotation and interfaces from javax.persistence package, without using the hibernate import packages.
We recommend using JPA annotations as we are not tied to Hibernate as implementation. Later (I know - <1% Chance), we can use another JPA implementation.
Q : Compare Entity Manager vs SessionFactory
Notes
- Entity Manager and SessionFactory are similar, have very similar responsibilities.
- JPA specifies EntityManager while Hibernate can work with both SessionFactory and EntityManager.
We recommend using pure JPA i.e. EntityManager. You would not want to be tied to Hibernate as the JPA implementation - Hence avoid SessionFactory.
Q : In which layer, should the boundary of a transaction start?
We recommend managing transactions in the Service layer. Logic for business transactions is in the business/service layer and you would want to enforce transaction management at that level.
Q : HQL vs JPQL
JPQL is a Java EE Standard. Once you use JPQL you can switch between any JPA implementation - Hibernate or Toplink or …
HQL is specific to Hibernate. If you use HQL, you are tied to Hibernate for your lifetime.
While this might seem not to be such a important choice now, what if there is a more popular JPA implementation in 5 years and you want to switch away from Hibernate. Applications using JPQL will be easier to migrate than those using HQL.
Q : What are the dependencies need to start up an in memory database H2 with Spring Boot?
In a Spring Boot project, you should be able to launch up H2 Console as long as you ensure the following dependencies are on the class path.
- web starter
- h2
- data jpa starter
The exact dependencies are shown below:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
A few tips:
- An in-memory database is live only during the time of execution of the application. It is an efficient way to learn a framework.
- This is not how you want your real world applications to behave.
- We explain how to connect to a database of your choice in the answer to the question “How do we connect to a external database?”.
Q : How is Hibernate chosen as the default implementation for JPA without any configuration?
Again - Spring Boot Auto Configuration.
This is the dependency we added in
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
The Starter spring-boot-starter-data-jpa has a transitive dependency on Hibernate and JPA.
When Spring Boot sees Hibernate in the class path, it auto configures it as the default JPA Implementation.
Q : Why H2? And how does it work?
First and most important thing - Spring Boot is intelligent.
If you are talking to an in memory db, by default, it looks at the entities and creates the database and the tables.
However, if you connect to a mysql database, Spring Boot knows that its a permanent database. By default, it expects you to set up the database, set up the tables and it uses the connection that you established.
Here are the details
- http://www.springboottutorial.com/spring-boot-auto-configuration
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/howto-database-initialization.html
Q : Where is the database connection info specified? How does it know to automatically connect to H2?
Thats Spring Boot Autoconfiguration magic.
From https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/using-boot-auto-configuration.html
“Spring Boot auto-configuration attempts to automatically configure your Spring application based on the jar dependencies that you have added. For example, If HSQLDBis on your classpath, and you have not manually configured any database connection beans, then we will auto-configure an in-memory database.
More Reading
- http://www.springboottutorial.com/spring-boot-auto-configuration
Q : How do we connect to a external database like MSSQL or oracle?
Let’s consider one of those as an example - MySQL
Step 1 - Add dependency for mqsql connector to pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
Step 2 - Remove H2 Dependency from pom.xml
Or atleast make its scope as test
<!--
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
-->
Step 3 - Setup your My SQL Database
- For more check out - https://github.com/in28minutes/jpa-with-hibernate#installing-and-setting-up-mysql
Step 4 - Configure your connection to My SQL Database
Configure application.properties
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=none
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/todo_example
spring.datasource.username=todouser
spring.datasource.password=YOUR_PASSWORD
Step 5 - Restart and You are ready!
That’s it
Q : What is the default h2 database name configured by Spring Boot? Why is the default database name testdb?
This is where all the default values in application.properties are listed
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/common-application-properties.html
Look for the property below
spring.datasource.name=testdb # Name of the datasource.
If you are using an H2 in-memory database, thats exactly the name that Spring Boot uses to setup your H2 database.
Q : What happens if H2 is not in the classpath?
You get this error
Cannot determine embedded database driver class for database type NONE
Add H2 to the pom.xml and Restart your server
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
Q : Why the data lost between restart?
H2 is an in memory database. Its not a persisted database.
H2 is a great tool for learning because you need zero setup.
While we dont recommend this , it interesting to note that H2 has a persisted database mode.
- With this configuration, the data is not lost even after spring boot restart and computer restart.
- You would find H2 being very rarely used in this way. If you are really interested in a persistent database, I would recommend MySQL
application.properties
spring.datasource.name=yourdbname
spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.initialize=false
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:file:~/yourdbname;DB_CLOSE_ON_EXIT=FALSE;IFEXISTS=TRUE;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1;
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
Error : Table is not created automatically in h2 embedded db or I’m unable to see the tables
Usually, the table’s are created but the url used in H2 GUI Console is wrong.
In the browser, change the database url to jdbc:h2:mem:testdb (Shown in the screen below).
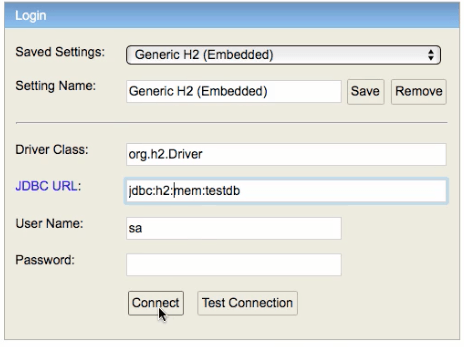
You should be good to go!
Error : H2 Console is not Launched up?
Try enabling it in the application.properties
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
Q : How did the insert query from data.sql run at application startup?
Thats the magic of Spring Boot Autoconfiguration again. You can read more here.
- http://www.springboottutorial.com/spring-boot-auto-configuration
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/howto-database-initialization.html
Q : How to define a Composite Primary Key or a Composite ID?
You can use a structure similar to below:
@Entity
public class Project {
@EmbeddedId ProjectId id;
}
@Embeddable
class ProjectId implements Serializable{
int departmentId;
long projectId;
}
Q : Why should we annotate EntityManager with @PersistenceContext and not just @Autowired?
It is actually recommended to use @PersistenceContext. It is a JPA Specific Specialization.
You can read more here
- https://docs.oracle.com/javaee/7/api/javax/persistence/PersistenceContext.html
Q : How can we connect to Multiple Databases using Spring Boot?
Here’s a good article showing how to connect to multiple databases
- http://www.baeldung.com/spring-data-jpa-multiple-databases
You have to do all the work now. You cannot depend on auto configuration :)
Here’s another good read:
- https://medium.com/@joeclever/using-multiple-datasources-with-spring-boot-and-spring-data-6430b00c02e7
Q : How did JdbcTemplate achieve connection details?
Its down to Spring Boot Auto Configuration!
First thing you would need to understand is Spring Boot Auto Configuration.
Here’s a good read
- http://www.springboottutorial.com/spring-boot-auto-configuration
As far as H2 is concerned, as soon as Spring Boot sees H2 in the class path, it auto configures something similar to what you see below:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb
spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
It knows that you are using an inmemory database H2 and It knows the default url if you don’t provide one.
Q : Can you give an example for ReadOnly as true in Transaction management?
- When you read stuff from the database, user details or any other details, you wanna set read only on the transaction so that Hibernate does not need to check for changes to the entities. This is more efficient.
Error : org.hibernate.loader.MultipleBagFetchException
Caused by: org.hibernate.loader.MultipleBagFetchException: cannot simultaneously fetch multiple bags: [com.mypackage.jpa.hibernate.jpahibernate.entity.Student.courses, com.mypackage.jpa.hibernate.jpahibernate.entity.Course.reviews]
It looks like this is a bug with Hibernate. Hibernate doesn’t like two collections with FetchType.EAGER
This thread is a good start for more approaches - https://stackoverflow.com/questions/4334970/hibernate-cannot-simultaneously-fetch-multiple-bags
Error : BeanCreationException - java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: At least one JPA metamodel must be present
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name ' ': Invocation of init method failed; nested exception is java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: At least one JPA metamodel must be present!
This is because of conflicts with older version of Hibernate.
Ensure you are using the recommended version of Spring Boot - 2.3.1.RELEASE
Q : Is it mandatory to specify @Repository on a repository which is extending JPARepository?
- Ideally you don’t need to have an @Repository. But, I faced a few issues sometimes - better be safe than sorry.
Q : JPA and Hibernate Course - Notes from Rodolfo
Link to this file: https://s3.amazonaws.com/espanol-libros/AllLinks.rtf
https://s3.amazonaws.com/espanol-libros/JPA/Section+5+JPA+and+Hibernate+in+Depth.rtf
https://s3.amazonaws.com/espanol-libros/JPA/Section+6+Establishing+Relationship+with+JPA+and+Hibernate+OneToOne.rtf
https://s3.amazonaws.com/espanol-libros/JPA/Section+7+Review+with+FAQs.rtf
https://s3.amazonaws.com/espanol-libros/JPA/Section+8+Establishing+relationships+with+JPA+and+Hibernate+ManyToOne.rtf
Q : How can we use a mysql database for running the application and use inmemory database H2 for unit tests?
The standard properties file that Spring Boot picks up automatically when running an application is called application.properties and resides in the src/main/resources folder.
If we want to use different properties for tests, then we can override the properties file in the main folder by placing another file with the same name in src/test/resources.
The application.properties file in src/test/resources folder should contain the standard key-value pairs necessary for configuring a in memory connection.
First add the dependencies for your database driver (mysql in the example below) and make the dependency for h2 test scoped.
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Use the mysql database for your real code
src\main\resources\application.properties
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=none
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/person_example
spring.datasource.username=personuser
spring.datasource.password=YOUR_PASSWORD
Use in memory database for your unit tests
src\test\resources\application.properties
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=sa
Q : When is any primary or an id field annotated with @GeneratedValue autogenerated? Why are we passing the value for id in data.sql?
Let’s consider a simple example:
@Entity
public class Course {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
Id is generated only when you insert it using entity manager.
Course course1 = new Course("Web Services in 100 Steps");
em.persist(course1);
When we use data.sql to insert the data we have to provide all the details as entity manager is not involved.
insert into course(id, name, created_date, last_updated_date,is_deleted)
values(10001,'JPA in 50 Steps', sysdate(), sysdate(),false);
Q : Field dao in SpringRestController required a bean of type ‘CustomerDAO’ that could not be found. Consider defining a bean of type ‘CustomerDAO’ in your configuration.
Two things that are typically a problem
- Annotate repository class with @Repository
- Try adding the annotation @EnableJpaRepositories(basePackageClasses = …) with the right value for basePackageClasses next to @SpringBootApplication on the Spring Boot Application class.
Error : Detached object passed to persist
Consider the code
public void playWithEntityManager() {
Course course = new Course( 200L, "Some Course" );
em.persist( course);
}
This is because an id on the Course is set - 200L. To fix it you can create a new constructor without an id and use it!
Hibernate distinguishes between transient and detached objects and persist works only with transient objects. If persist concludes the object is detached (which it will because the ID is set), it will return the “detached object passed to persist”
Error : java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: javax/wsdl/extensions/ExtensibilityElement
SOAP Web Service - ationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext
Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'courses' defined in class path resource [com/ashwani/CustomerDetailsService/WebServiceConfig.class]: Bean instantiation via factory method failed; nested exception is org.springframework.beans.BeanInstantiationException: Failed to instantiate [org.springframework.ws.wsdl.wsdl11.DefaultWsdl11Definition]: Factory method 'defaultWsdl11Definition' threw exception; nested exception is java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: javax/wsdl/extensions/ExtensibilityElement
Make sure you have this dependency in the pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>wsdl4j</groupId>
<artifactId>wsdl4j</artifactId>
</dependency>
Q : How do authentication with jwt to service REST??
I’m working on a course for Full Stack Developer with REST APIs (on Spring Boot) connecting to a frontend (Angular and React) and this is exactly the stuff that needs attention.
Here’s a good reference - https://medium.com/@nydiarra/secure-a-spring-boot-rest-api-with-json-web-token-reference-to-angular-integration-e57a25806c50
Unit Testing
Q : What is a mockito answer?
Here’s a great starting point https://testing.googleblog.com/2014/03/whenhow-to-use-mockito-answer.html
Q : How do you mock a private method that requires arguments?
PowerMockito.when(SomeClass.class, "somePrivateMethodName", argument1, argument2).thenReturn(returnValue);
Q : How to make JUnit run at regular intervals of time?
I love Infinitest - https://infinitest.github.io/
This keeps running your unit tests in the back ground. You can focus on your code.
Q : Annotation Changes - JUnit 4 vs JUnit 5
Annotation Changes in JUnit 5
- @Before annotation is renamed to @BeforeEach
- @After annotation is renamed to @AfterEach
- @BeforeClass annotation is renamed to @BeforeAll
- @AfterClass annotation is renamed to @AfterAll
- @Ignore annotation is renamed to @Disabled
You and in28Minutes
Q : What should you do to make the best use of our courses?
What is the use of all these numbers?
- 99000+ - Students!
- 7000+ - 5 Star Reviews on our Courses
- More than 100 Hours of Course Content
Not useful unless you make the best use of these.
Learn something new for atleast half an hour every day!
If you do it for 100 days consecutively, it becomes a habit. Good Habits are great things to have.
If you are not able to commit time on the courses, then read this - “The in28Minutes Way” - https://github.com/in28minutes/in28minutes-initiatives/tree/master/The-in28Minutes-Way
Open up your mobile and set a daily reminder now!
Q : Why should you learn from in28Minutes?
Read this - “The in28Minutes Way” - https://github.com/in28minutes/in28minutes-initiatives/tree/master/The-in28Minutes-Way
Some facts
- 75% - Percentage of New Java Projects/Microservices using Spring/Spring Boot
- 300% - Increase in Microservices using Spring Boot in the last two years!
- 70% - Percentage of Real World projects using Maven
- 70% - Percentage of Real World Projects using Git as Version Control. Fork, Like and Play!
- 10+ - We are in the world of Microservices. We create a number of small microservices. That means understand how to set up projects is a very important skill. We help you learn that by creating a number of small projects during this course.
- 80/20 - Most Important Rule that dictates things for in28Minutes.
Remember if you Listen, Watch, Do and Repeat. You Retain More of What you learn.
Once you realize the importance of what you are learning, committing to your goal becomes easy. Think and find at least 28 minutes in your day for doing this. Good Luck.
Q : What is the focus of each of your courses?
Here are the courses and their focus areas:
- Master Microservices with Spring Boot & Spring Cloud
- Expert - Microservices with Spring Cloud
- Setup Centralized Microservices Configuration with Spring Cloud Config Server
- Implement client side load balancing (Ribbon), Dynamic scaling(Eureka Naming Server) and an API Gateway (Zuul)
- Distributed tracing for microservices with Spring Cloud Sleuth and Zipkin
- Fault Tolerance for microservices with Hystrix
- Expert - RESTful API and Web Services with Spring Boot
- Best Practices in Designing RESTful web services
- Implement Exception Handling, Validation, HATEOAS and filtering for RESTful Web Services
- Version and Document (using Swagger) Your RESTful Web Services
- Introduction Modules
- Spring Boot
- JPA
- Expert - Microservices with Spring Cloud
- Master Web Services and REST API with Spring Boot
- Expert - SOAP Web Services with Spring Boot
- Understand WSDL, SOAP Header, SOAP Body, SOAP Fault, XSD, JAXB and EndPoint
- Use Contract First Approach to Develop Web Services
- Expert - Design and Develop RESTful API and Web Services with Spring Boot
- Best Practices in Designing RESTful web services
- Implement Exception Handling, Validation, HATEOAS and filtering for RESTful Web Services
- Version and Document (using Swagger) Your RESTful Web Services
- Connect web services to JPA/Hibernate
- Introduction Modules
- Spring Boot
- Expert - SOAP Web Services with Spring Boot
- Master Hibernate & JPA with Spring Boot in 100 Steps
- Expert - JPA & Hibernate with Spring Boot
- Fundametals - Entities, Relationships, Inheritance Mappings and Annotations
- Relationships in depth - One to One, Many to One and Many to Many
- Querying data - JPQL, Criteria API and Native Queries
- Caching - First Level Cache and Second Level Cache with EhCache
- Performance tuning your JPA application with Hibernate - Solve N+1 Queries Issue
- Introduction Modules
- Spring, Spring Boot, Spring JDBC, Spring Data JPA and Spring Data REST
- Expert - JPA & Hibernate with Spring Boot
- Learn Spring Boot in 100 Steps - Beginner to Expert
- Expert - Fundamentals of Spring Boot
- Magic of Spring Boot - Auto Configuration, Spring Initializr and Starter Projects
- Develop a Web Application connecting to JPA/Hibernate Step by Step with Spring MVC and Spring Boot
- Understand Spring MVC in depth - DispatcherServlet , Model, Controllers and ViewResolver
- Externalise application configuration using Spring Boot Profiles and Dynamic Configuration
- Monitoring
- Write great Unit and Integration tests using Spring Boot Starter Test
- Use a wide variety of Spring Boot Starter Projects - Spring Boot Web, Spring Boot Test, Spring Boot Data JPA, Spring Boot Data REST
- Explore the embedded servlet container options provided by Spring Boot - Tomcat, Jetty and Undertow
- Make best use of Spring Boot Actuator and Spring Boot Developer Tools
- Introduction Modules
- Spring, JUnit and Mockito.
- Expert - Fundamentals of Spring Boot
- Spring Master Class - Beginner to Expert in 100 Steps
- Expert - Fundamentals of Spring Framework
- Dependency Injection, IOC Container, Application Context and Bean Factory.
- Spring Annotations - @Autowired, @Component, @Service, @Repository, @Configuration, @Primary
- Unit tests with XML, Java Application Contexts and Mockito
- Introduction Modules
- Maven, JUnit, Mockito and Spring Boot
- Expert - Fundamentals of Spring Framework
Q : How to improve Logical Skills?
Logical skills are difficult to acquire but are among the things which will help you through out your programming career.
There are three ways - Practice, Practice and More Practice.
I would suggest joining a programming contest like CodeChef or TopCoder for a start. Once you start being active there, you will understand everything else.