Through examples, this guide will help you understand Spring Boot Auto Configuration. We will create a few basic REST services using simple code samples.
What You Will Learn
- Why Auto Configuration is needed in Spring Boot
- What Auto Configuration actually is
- Examples of Spring Boot Auto Configuration in action
- How Auto Configuration is implemented under the hood
- Techniques to debug Auto Configuration
Tools You Will Need
- Maven 3.0+ – Build tool for your Spring Boot project
- IDE – Your favorite IDE; we recommend Eclipse or IntelliJ IDEA
- JDK 17+ – Java Development Kit for compiling and running the application
Complete Maven Project with Code Examples
Our GitHub repository contains all the code examples: https://github.com/in28minutes/in28minutes.github.io/tree/master/code-zip-files
- Restful Web Services Examples
Website-springbootrestservices-all-examples.zip
Why Do We Need Spring Boot Auto Configuration?
Spring-based applications often require extensive configuration.
For example, in a typical Spring MVC application, you need to configure:
- Component scanning
- Dispatcher Servlet
- View resolver
- WebJars (for serving static content)
- And other required beans and settings
Spring Boot Auto Configuration helps reduce this boilerplate by automatically configuring many of these components for you.
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix">
<value>/WEB-INF/views/</value>
</property>
<property name="suffix">
<value>.jsp</value>
</property>
</bean>
<mvc:resources mapping="/webjars/**" location="/webjars/"/>
A typical configuration of a Dispatcher Servlet in a Spring web application is shown in the code snippet below.
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/todo-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
When using Hibernate/JPA, you need to configure a data source, an EntityManagerFactory, and a transaction manager, among other components.
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClass" value="${db.driver}" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${db.url}" />
<property name="user" value="${db.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${db.password}" />
</bean>
<jdbc:initialize-database data-source="dataSource">
<jdbc:script location="classpath:config/schema.sql" />
<jdbc:script location="classpath:config/data.sql" />
</jdbc:initialize-database>
<bean
class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean"
id="entityManagerFactory">
<property name="persistenceUnitName" value="hsql_pu" />
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager">
<property name="entityManagerFactory" ref="entityManagerFactory" />
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
The examples shown here are representative of typical Spring Framework setups or integrations with other frameworks.
Spring Boot: Can We Think Differently?
Spring Boot introduces a new approach to application development, simplifying configuration and reducing boilerplate code.
Can we make this smarter? For example, when a Spring MVC JAR is added to an application, can certain beans be auto-configured automatically without explicit setup by the developer?
- Automatically configure a Data Source if the Hibernate JAR is present on the classpath.
- Automatically configure a Dispatcher Servlet if the Spring MVC JAR is present on the classpath.
There are provisions to override the default autoconfiguration when custom behavior is needed.
Spring Boot inspects:
- The frameworks present on the classpath
- The current settings of the application
Based on these, Spring Boot provides the necessary default configurations to set up the application with the detected frameworks. This process is called Auto Configuration.
To explore Auto Configuration in action, let’s bootstrap a simple Spring Boot application using Spring Initializr.
Creating a REST Services Application with Spring Initializr
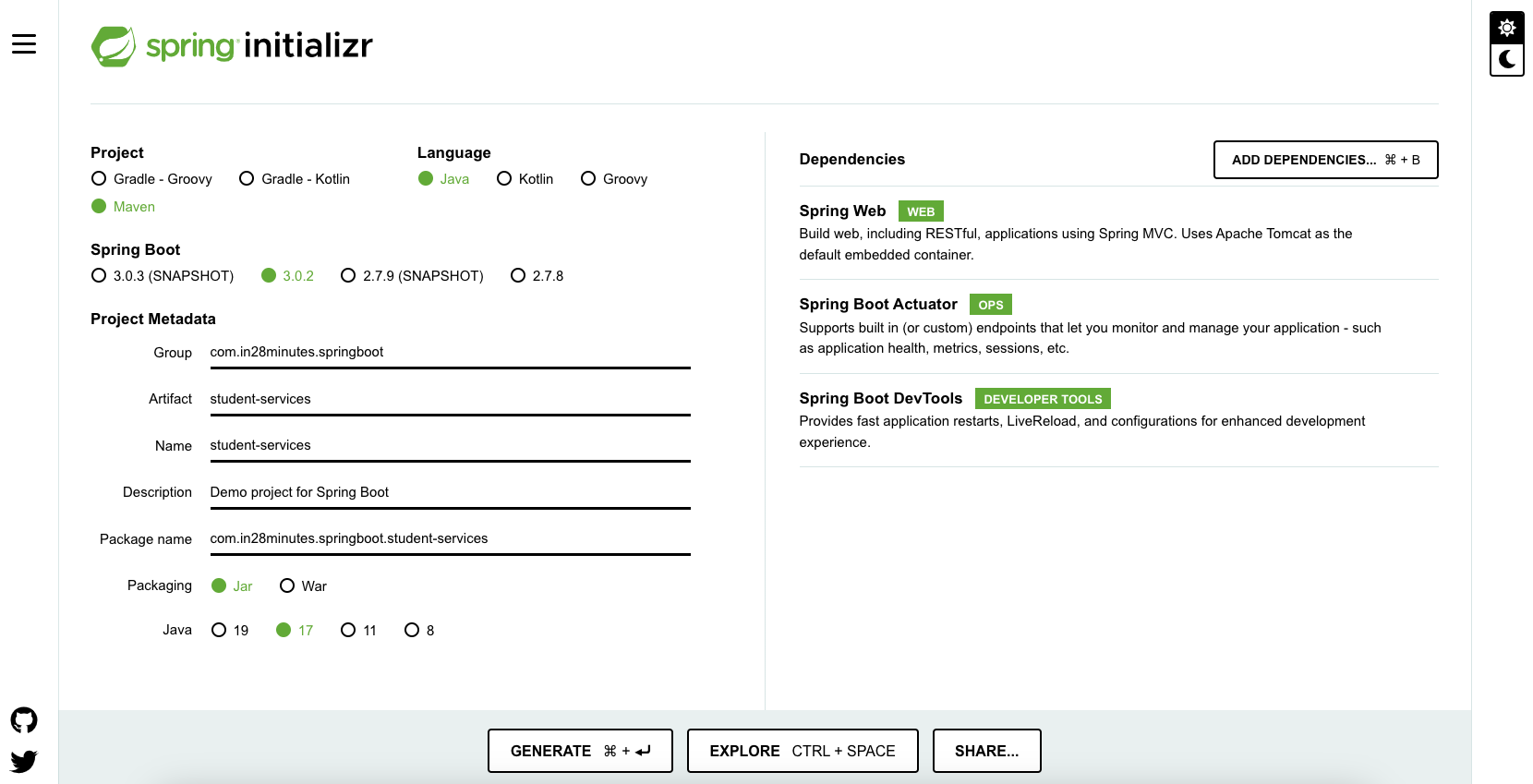
Spring Initializr http://start.spring.io/ is a powerful tool to quickly bootstrap your Spring Boot projects.

As shown in the image above, follow these steps to bootstrap your Spring Boot project:
- Launch Spring Initializr and configure the project:
- Group:
com.in28minutes.springboot - Artifact:
student-services - Dependencies:
- Web
- Actuator
- DevTools
- Group:
- Click Generate Project.
- Import the generated project into Eclipse.
- To understand all the files included in this project, refer to the provided documentation.
Spring Boot Auto Configuration in Action
When you run StudentServicesApplication.java as a Java application, you will notice several important messages in the log that demonstrate Spring Boot’s auto-configuration at work.
- **Mapping servlet**: `'dispatcherServlet'` is mapped to `/`
- **Error mapping**: `{/error}` is mapped to the `BasicErrorController.error()` method
- **WebJars mapping**: `/webjars/**` is mapped to the `ResourceHttpRequestHandler` for serving static resources
The log statements above are excellent examples of Spring Boot Auto Configuration in action.
Spring Boot auto-detects that Spring MVC is on the classpath when you include Spring Boot Starter Web as a dependency. It automatically configures:
dispatcherServlet- A default error page
- WebJars for serving static resources
Similarly, when you add Spring Boot Data JPA Starter, Spring Boot Auto Configuration automatically sets up a DataSource and an EntityManager.
Where is Spring Boot Auto Configuration Implemented?
The JAR spring-boot-autoconfigure.jar contains all the autoconfiguration logic.
It provides configuration for MVC, Data, JMS, and other Spring frameworks in a single place.

/META-INF/spring.factories is another crucial file contained within spring-boot-autoconfigure.jar. This file contains a list of all the auto configuration classes that should be imported using the AutoConfigurationImportFilter and AutoConfigurationImportFilter keys, depending on the dependencies found on the classpath.
# Auto Configuration Import Listeners
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportListener=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener
# Auto Configuration Import Filters
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnWebApplicationCondition
Example of Auto Configuration
Let’s take a look at DataSourceAutoConfiguration.
Typically, all autoconfiguration classes check which classes are available on the classpath. If certain classes are present, Spring Boot enables the corresponding configuration automatically.
Annotations such as:
@ConditionalOnClass@ConditionalOnMissingBean
help provide this conditional autoconfiguration behavior.
@ConditionalOnClass({ DataSource.class, EmbeddedDatabaseType.class }) : This configuration is enabled only when these classes are available in the classpath.
@AutoConfiguration(
before = {SqlInitializationAutoConfiguration.class}
)
@ConditionalOnClass({DataSource.class, EmbeddedDatabaseType.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
type = {"io.r2dbc.spi.ConnectionFactory"}
)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({DataSourceProperties.class})
@Import({DataSourcePoolMetadataProvidersConfiguration.class})
public class DataSourceAutoConfiguration {
@ConditionalOnMissingBean : This bean is configured only if there is no other bean configured with the same name.
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public DataSourceInitializer dataSourceInitializer() {
return new DataSourceInitializer();
}
An embedded database is configured only if no beans of type DataSource.class or XADataSource.class are already defined in the application context.
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Conditional({EmbeddedDatabaseCondition.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({DataSource.class, XADataSource.class})
@Import({EmbeddedDataSourceConfiguration.class})
protected static class EmbeddedDatabaseConfiguration {
protected EmbeddedDatabaseConfiguration() {
}
}
Debugging Auto Configuration
There are two main ways to debug and get more information about Spring Boot auto-configuration:
- Enable debug logging
- Use Spring Boot Actuator
Debug Logging
You can enable debug logging by adding a property to application.properties.
For example, the configuration below turns on DEBUG level logging for all classes in the org.springframework package and its subpackages:
logging.level.org.springframework=DEBUG
When you restart the application, an autoconfiguration report will be printed in the logs.
The report lists all autoconfiguration classes, separating positive matches from negative matches.
It shows:
- Why a particular bean was autoconfigured
- Why certain beans were not autoconfigured
=========================
CONDITIONS EVALUATION REPORT
=========================
Positive matches:
-----------------
DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.DispatcherServletConfiguration matched:
- @ConditionalOnClass found required class 'jakarta.servlet.ServletRegistration' (OnClassCondition)
- Default DispatcherServlet did not find dispatcher servlet beans (DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.DefaultDispatcherServletCondition)
Negative matches:
-----------------
ArtemisAutoConfiguration:
Did not match:
- @ConditionalOnClass did not find required class 'jakarta.jms.ConnectionFactory' (OnClassCondition)
AopAutoConfiguration.ClassProxyingConfiguration:
Did not match:
- @ConditionalOnMissingClass found unwanted class 'org.aspectj.weaver.Advice' (OnClassCondition)
Spring Boot Actuator
Another way to debug autoconfiguration is by adding Spring Boot Actuator to your project.
We can also include HAL Explorer to simplify browsing and exploring actuator endpoints.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-rest-hal-explorer</artifactId>
</dependency>
HAL Explorer autoconfiguration http://localhost:8080/actuator/conditions would show the details of all the beans which are autoconfigured and those which are not.