In this article, we will describe the first steps, in taking an architecture from monolith to microservice.
You will learn
- What are the important features of microservices architectures?
- What are the important challenges?
- How do you break a monolith to microservices?
Let’s start with the basics of a monolith architecture, understand the microservices architecture, and figure out what should you do to migrate from the former to the latter.
Monolith Architecture
The salient features of monolith applications are:
- Released, or taken to production, once every few week or months or years
- Generally have a wide range of features and functionality
- Have a development team of over 50 people working on them
- Debugging problems that arise in them, is a huge challenge
- It is almost impossible to bring in new technologies and technical processes, midway through the lifetime of such an application
Monolith applications are typically huge, with them having a million lines of code on average.
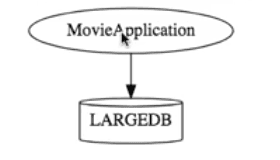
A monolithic application would look something like the following:
You have a large application talking to a large database.
Microservices Architecture
In microservices architectures, instead of building a large application, we build a number of smaller microservices.
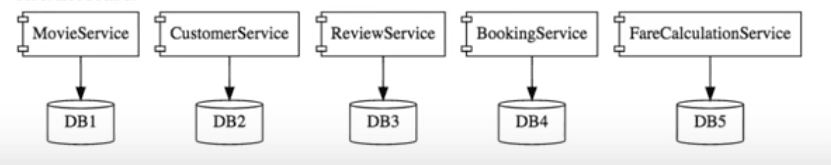
Here is how you would split up the monolith MovieApplication:
As you can see here, the databases are also separated out.
Microservices architecture involves a number of small, well-designed microservices, that exchange messages among themselves:
Microservices Architecture Is Tough
While a microservices architecture looks very easy at a high level, implementing it is not a trivial process at all.
There are a number of important decisions to make for moving to Microservices Architectures
Examples:
- What are the boundaries of the individual microservices?
- How small should a microservice be, and what functionality should go into it?
- What all data needs to go into the database that a particular microservice talks to extensively?
- How should the microservices communicate with each other?
Challenges with the Microservices Architectures
The challenges that need to be tacked when setting up a microservices architecture are described below.
Quick Setup Needed
You can NOT spend a month setting up each microservice. You should be able to setup a microservice quickly.
Automation
Because there are a number of smaller components instead of a monolith, there needs to be automation in every activity, such as builds, deployment, monitoring, etc.
Visibility
You have a potentially large number of smaller components to deploy and maintain. This number could be 100 today, and a 1000 tomorrow. You should be able to monitor and identify problems automatically. You need great visibility around all the components.
Bounded Context
Deciding the boundaries of a microservice is not an easy task. Applying Bounded Context principles from Domain Driven Design is usually a good starting point.
Your understanding of the domain evolves over a period of time. You need to ensure that the microservice boundaries evolve with time.
Configuration Management
You need to maintain configurations for hundreds of components across environments. It would be best to have a configuration management solution.
Dynamic Scale Up And Scale Down
The advantages of a microservices architecture can be realized only of the application can scale up and scale down easily in the cloud.
Pack Of Cards
If the microservice at the bottom of a call chain fails, it can have knock on effects on all the other microservices. Microservices should be fault tolerant by design.
Debugging
When there is a problem that needs investigation, you might need to look into multiple services across different components. Centralized logging ans dashboards are essential to make it easy to debug problems.
Consistency
You cannot have a wide range of tools solving the same problem. While it is important to encourage innovation, it is also essential to have decentralized governance around the languages, platforms, technologies and tools used for implementing, deploying and monitoring microservices.
Going from Monolith To Microservices - It is Not A Switch
You may have noticed that after describing monolith applications, we directly jumped into the challenges of microservices.
The reason we did not first talk about the advantages of microservices, is that you need a reality check when you migrate from one architecture to another. You need to realize this is not something you can do in a few weeks or months.
Getting a microservices architecture right involves a few years of work. It’s not a switch, but a journey.
During that journey, both architectures live side by side.
You would hope that number of applications using the microservices architecture grows over time.
Ask Why are you migrating From Monolith To Microservices
This is the most important question to ask! Don’t do microservices because it is a buzzword. Do it because your business needs it.
Why are you migrating from Monolith to Microservices?
What do you want to achieve?
- Do you want to be able to adopt new technologies and processes, in a faster manner?
- Do you want faster release cycles for your application?
- Do you want to scale more easily in the cloud?
You need to be very aware of which of these reasons is the biggest one, for your migration.
The approach you use to actually migrate would differ, based on the exact reason for migration.
Let’s look at these approaches in a little more detail.
If your reason is - to Adopt New Technologies
Let’s say the reason is the ability to adopt newer technologies. In that case, you can start off with designing microservices for the next set of features you intend to implement. In other words, all the requirements for new feature implementation in the monolith application, are the best candidates to become microservices.
You need to answer questions such as:
- How do you design the database?
- How do make sure the communication between the old monolith and the new components, is proper?
If your reason is - to have Faster Release Cycles
Your business may not be happy with the pace at which new features are being released to production. In that scenario, you first need to identify those parts of the application, where there are frequent changes.
Once you do this, you can extract the fast moving parts and create microservices around them.
The idea behind this is , when there is a change, only release the related microservice.
If your reason is - to Scale With The Cloud
If the driving force behind the migration is scaling with the cloud, then you need to analyze what needs to be done to put your application in the cloud.
Start with research and Proof-of-Concept prototypes to understand the dependencies involved. You need to find out which dependencies are important to break, and anticipate the problems you may face on making the application cloud-native.
More than one
Your business might need more that one of the above. Prioritize them and get started with the most important ones.
Clearly, the path to migration will not be the same for all. However, with whatever microservices that you design in your journey, make sure they address the challenges that we saw earlier, in an effective manner.
Do check out our video on this:
Summary
In this article, we had a good look at the activities involved in moving from a monolith to a microservices architecture. We observed that it is not an easy journey, as the though process involved in designing the two kinds of systems, is radically different.
The actual journey of your migration will heavily depend upon the exact reason why you want to do it. Ultimately, with whatever microservices you come up with, make sure they effectively address the challenges that exist in such a system.