This guide will help you create a SOAP Web Service with Spring Boot Starter Web Services. We will take a Contract First approach by definining an XSD and exposing a WSDL from it.
You will learn
- What is a web service?
- What are the different types of web services?
- What is SOAP Web Service?
- What is SOAP?
- What is a SOAP Envelope?
- What is SOAP Header and SOAP Body?
- What is WSDL (Web Service Definition Language)?
- What are the different parts of a WSDL?
- What is Contract First Approach?
- What is an XSD?
- What is JAXB?
- How do you configure a JAXB Plugin?
- What is an Endpoint?
- Can you show an example endpoint written with Spring Web Services?
- What is a MessageDispatcherServlet?
- How do you configure a MessageDispatcherServlet?
- How do you generate a WSDL using Spring Web Services?
Resources Overview
In this guide, we will create a Student Resource exposing three services using proper URIs and HTTP methods:
- Retrieve all Students - @GetMapping(“/students”)
- Get details of specific student - @GetMapping(“/students/{id}”)
- Delete a student - @DeleteMapping(“/students/{id}”)
- Create a new student - @PostMapping(“/students”)
- Update student details - @PutMapping(“/students/{id}”)
Project Code Structure
Following screenshot shows the structure of the project we will create.
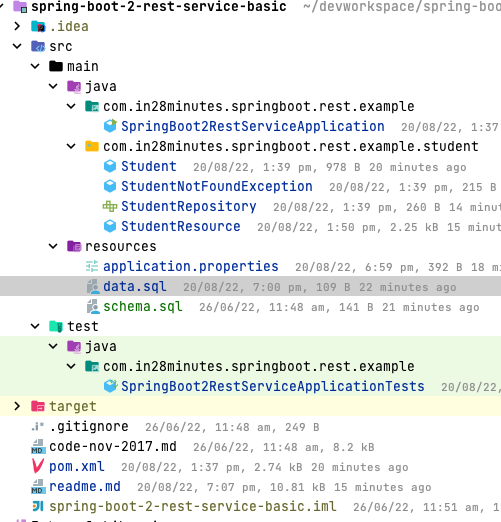
A few details:
- SpringBoot2RestServiceApplication.java - The Spring Boot Application class generated with Spring Initializer. This class acts as the launching point for application.
pom.xml- Contains all the dependencies needed to build this project. We will use Spring Boot Starter AOP.Student.java- Student JPA Entity- StudentRepository.java - Student JPA Repository. This is created using Spring Data JpaRepository.
- StudentResource.java - Spring Rest Controller exposing all services on the student resource.
- data.sql - Initial data for the student table. Spring Boot would execute this script after the tables are created from the entities.
Tools you will need
- Maven 3.0+ is your build tool
- Your favorite IDE. We use Eclipse.
- JDK 1.8+
Complete Maven Project With Code Examples
Our Github repository has all the code examples - https://github.com/in28minutes/spring-boot-examples/tree/master/spring-boot-tutorial-soap-web-services
What is a Web Service?
Service delivered over the web
Is this really a complete definition. Is everything thats delivered over the web “Web Service”?
The key things to understand is
- Web services are designed for machine-to-machine (or application-to-application) interaction
- Web services should be interoperable - Not platform dependent
- Web services should allow communication over a network
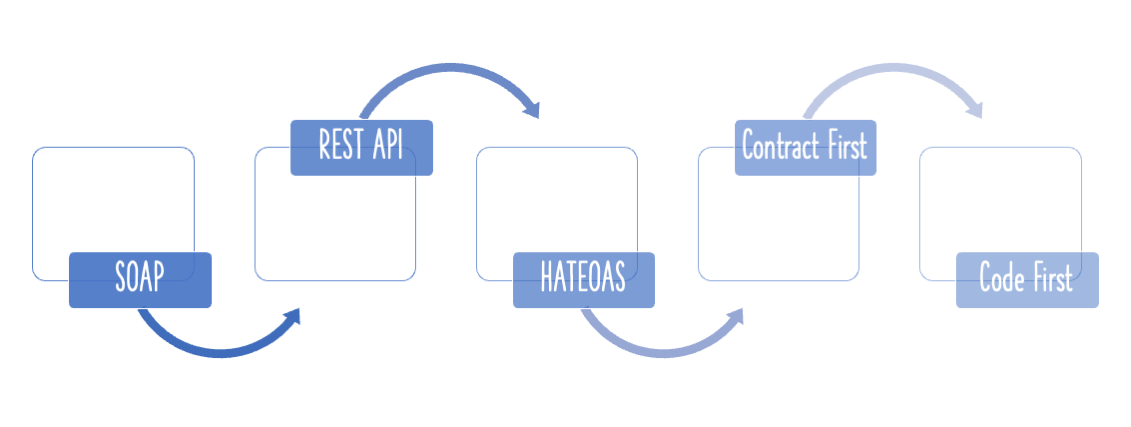
Types of Web Services
Not really types but a broad classification
- SOAP
- REST
These are not really mutually exclusive. Some SOAP services can actually be RESTful.
SOAP
SOAP was earlier an abbreviation for Simple Object Access Protocol. In SOAP, the request and response are in XML format. However, not all types of XML are valid SOAP Requests.
SOAP defines a standard XML format. We will use WSDL (Web Service Definition Language) to define the format of request xml and the response xml.
Now lets say Facebook wants to know how to call the TODO Service? What should I give to the Facebook developer?
I will give him a WSDL of the Todo service. It will explain:
- What are the different services (operations) exposed by the server?
- How can a service (operation) be called? What url to use? (also called End Point).
- What should the structure of request xml?
- What should be the structure of response xml?
SOAP format defines a SOAP-Envelope which envelopes the entire document.
- SOAP-Header (optional) contains any information needed to identify the request. Also, part of the Header is authentication, authorization information (signatures, encrypted information etc).
- SOAP-Body contains the real xml content of request or response.
- In case of error response, server responds back with SOAP-Fault.
REST vs SOAP
REST vs SOAP are not really comparable. REST is an architectural style. SOAP is a message exchange format.
Let’s compare the popular implementations of REST and SOAP styles.
- RESTful Sample Implementation : JSON over HTTP
- SOAP Sample Implementation : XML over SOAP over HTTP
Following are the important things to consider:
- REST is built over simple HTTP protocol. SOAP services are more complex to implement and more complex to consume.
- REST has better performance and scalability. REST reads can be cached, SOAP based reads cannot be cached.
- REST permits many different data formats (JSON is the most popular choice) where as SOAP only permits XML.
- SOAP services have well defined structure and interface (WSDL) and has a set of well defined standards (WS-Security, WS-AtomicTransaction and WS-ReliableMessaging). Documentation standards with REST are evolving(We will use Swagger in this course).
SOAP Service Examples
Request
<Envelope xmlns="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<Body>
<getCourseDetailsRequest xmlns="http://in28minutes.com/courses">
<id>Course1</id>
</getCourseDetailsRequest>
</Body>
</Envelope>
Response
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<SOAP-ENV:Header/>
<SOAP-ENV:Body>
<ns2:getCourseDetailsResponse xmlns:ns2="http://in28minutes.com/courses">
<ns2:course>
<ns2:id>Course1</ns2:id>
<ns2:name>Spring</ns2:name>
<ns2:description>10 Steps</ns2:description>
</ns2:course>
</ns2:getCourseDetailsResponse>
</SOAP-ENV:Body>
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
Fault
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<SOAP-ENV:Header/>
<SOAP-ENV:Body>
<SOAP-ENV:Fault>
<faultcode>SOAP-ENV:Server</faultcode>
<faultstring xml:lang="en">java.lang.NullPointerException</faultstring>
</SOAP-ENV:Fault>
</SOAP-ENV:Body>
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
WSDL
WSDL is used to define the structure of Request and the Structure of Response.
- view-source:http://localhost:8080/ws/courses.wsdl
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?><wsdl:definitions xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/" xmlns:sch="http://in28minutes.com/courses" xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/" xmlns:tns="http://in28minutes.com/courses" targetNamespace="http://in28minutes.com/courses">
<wsdl:types>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified" targetNamespace="http://in28minutes.com/courses">
<xs:element name="getCourseDetailsRequest">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="id" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="getCourseDetailsResponse">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="course" type="tns:course"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:complexType name="course">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="id" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="name" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="description" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>
</wsdl:types>
<wsdl:message name="getCourseDetailsRequest">
<wsdl:part element="tns:getCourseDetailsRequest" name="getCourseDetailsRequest">
</wsdl:part>
</wsdl:message>
<wsdl:message name="getCourseDetailsResponse">
<wsdl:part element="tns:getCourseDetailsResponse" name="getCourseDetailsResponse">
</wsdl:part>
</wsdl:message>
<wsdl:portType name="CoursesPort">
<wsdl:operation name="getCourseDetails">
<wsdl:input message="tns:getCourseDetailsRequest" name="getCourseDetailsRequest">
</wsdl:input>
<wsdl:output message="tns:getCourseDetailsResponse" name="getCourseDetailsResponse">
</wsdl:output>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:portType>
<wsdl:binding name="CoursesPortSoap11" type="tns:CoursesPort">
<soap:binding style="document" transport="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http"/>
<wsdl:operation name="getCourseDetails">
<soap:operation soapAction=""/>
<wsdl:input name="getCourseDetailsRequest">
<soap:body use="literal"/>
</wsdl:input>
<wsdl:output name="getCourseDetailsResponse">
<soap:body use="literal"/>
</wsdl:output>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:binding>
<wsdl:service name="CoursesPortService">
<wsdl:port binding="tns:CoursesPortSoap11" name="CoursesPortSoap11">
<soap:address location="http://localhost:8080/ws"/>
</wsdl:port>
</wsdl:service>
</wsdl:definitions>
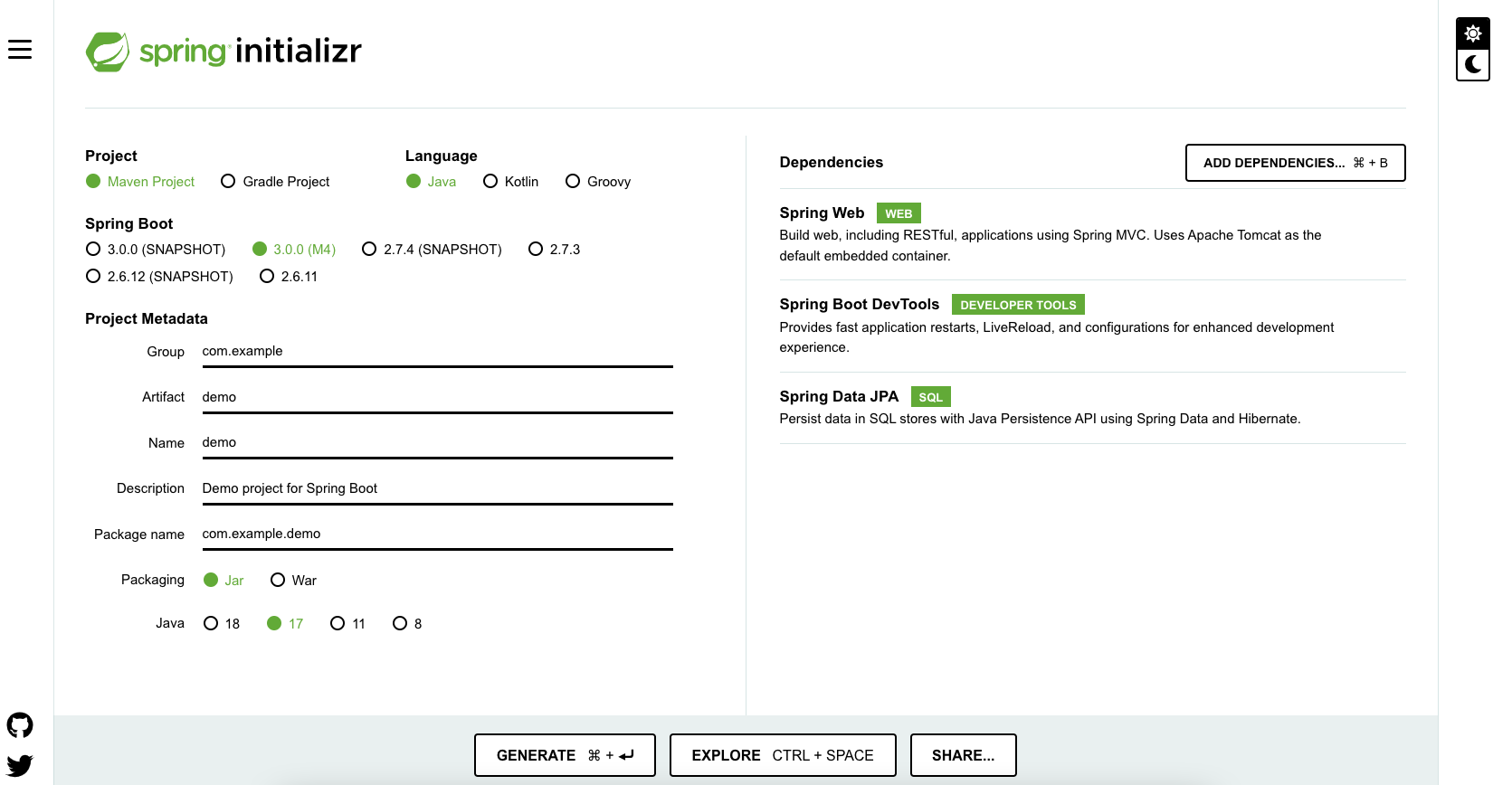
Bootstrapping with Spring Initializr
Creating a SOAP Web service with Spring Initializr is a cake walk.
Spring Initializr http://start.spring.io/ is great tool to bootstrap your Spring Boot projects.
You can create a wide variety of projects using Spring Initializr.
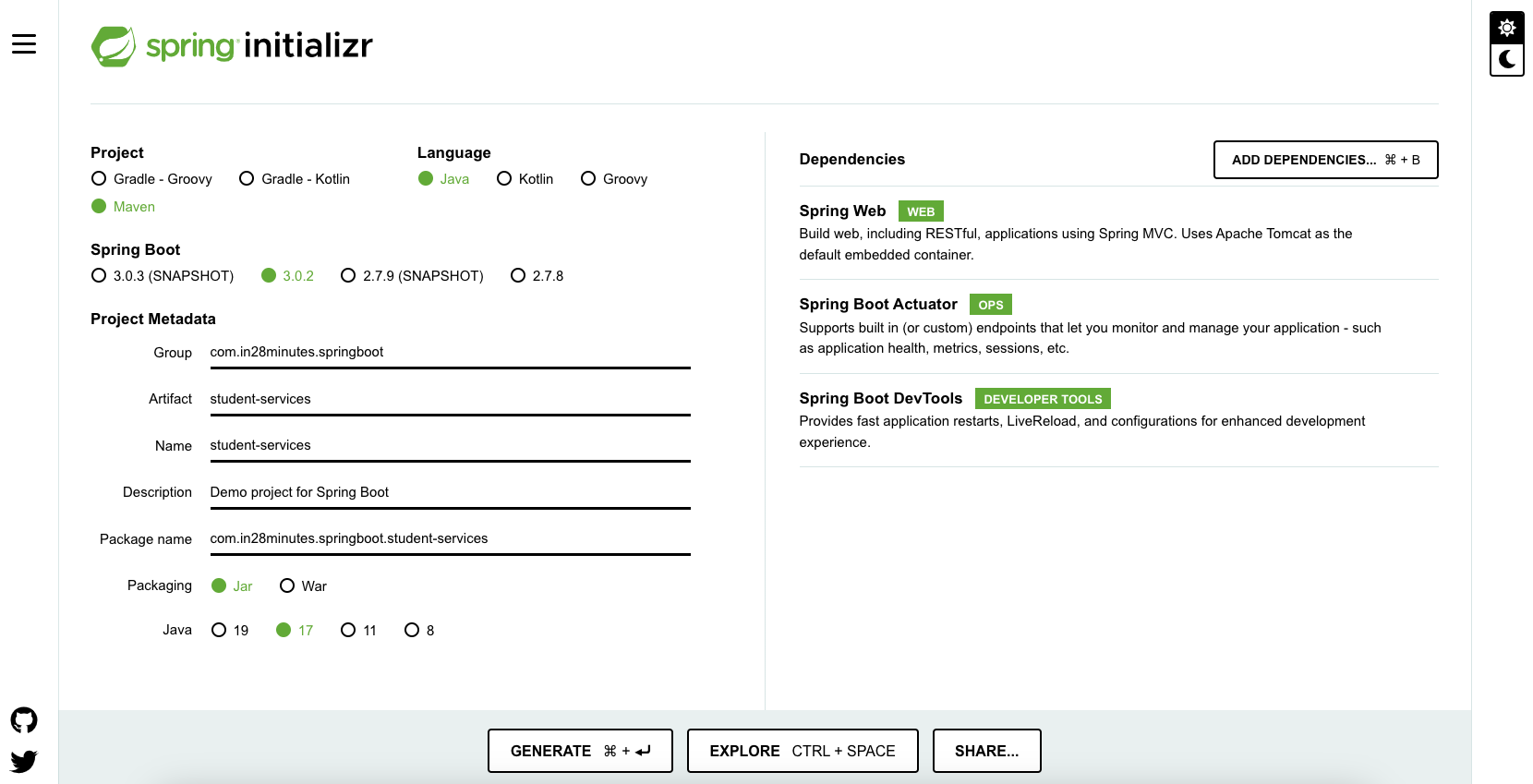

Following steps have to be done for a Web Services project
- Launch Spring Initializr and choose the following
- Choose
com.in28minutes.springboot.soap.web.services.exampleas Group - Choose
spring-boot-tutorial-soap-web-servicesas Artifact - Choose following dependencies
- Web Services
- DevTools
- Choose
- Click Generate Project.
- Import the project into Eclipse. File -> Import -> Existing Maven Project.
Do not forget to add Web Services as a dependency.
Creating a SOAP Web Service with Spring Boot
We will use a contract first approach and first define the XSD for the request and response.
Define XSD for Request and Response
/src/main/resources/student-details.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
targetNamespace="http://in28minutes.com/students"
xmlns:tns="http://in28minutes.com/students" elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xs:element name="GetStudentDetailsRequest">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name= "id" type="xs:int"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="GetStudentDetailsResponse">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name= "StudentDetails" type="tns:StudentDetails"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:complexType name="StudentDetails">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="id" type="xs:int"/>
<xs:element name="name" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="passportNumber" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>
We are create a simple xsd defining the request GetStudentDetailsRequest and the response GetStudentDetailsResponse.
Example request and response are shown below
Request
<Envelope xmlns="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<Body>
<GetStudentDetailsRequest xmlns="http://in28minutes.com/students">
<id>1</id>
</GetStudentDetailsRequest>
</Body>
</Envelope>
Response
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<SOAP-ENV:Header/>
<SOAP-ENV:Body>
<ns2:GetStudentDetailsResponse xmlns:ns2="http://in28minutes.com/students">
<ns2:StudentDetails>
<ns2:id>1</ns2:id>
<ns2:name>Adam</ns2:name>
<ns2:passportNumber>E1234567</ns2:passportNumber>
</ns2:StudentDetails>
</ns2:GetStudentDetailsResponse>
</SOAP-ENV:Body>
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
Java API for XML Binding (JAXB) and Configuring JAXB 2 Maven Plugin
When we implement our code using Spring Web Services, following are the steps that are typically involved in processing a request
- Map Request XML to Java Request Objects
- Do the business logic and create the Java Response Objects
- Map the Response Object to a Response XML and return the response.
We do mapping from XML to Java and Java to XML. This is done using JAXB - Java API for XML Binding.
A Maven JAXB Plugin helps us in generating the Java objects based on the XSD. Lets add it to our pom.xml.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb2-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.6</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>xjc</id>
<goals>
<goal>xjc</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
<configuration>
<schemaDirectory>${project.basedir}/src/main/resources</schemaDirectory>
<outputDirectory>${project.basedir}/src/main/java</outputDirectory>
<clearOutputDir>false</clearOutputDir>
</configuration>
</plugin>
Three important configurations
<schemaDirectory>${project.basedir}/src/main/resources</schemaDirectory>- The location of XSD files.<outputDirectory>${project.basedir}/src/main/java</outputDirectory>- Where do you want your Java code to be generated to?<clearOutputDir>false</clearOutputDir>- Should the output directory be cleaned every time? We use false because we write our java source code in the same directory.
Configuring an Endpoint for GetCourseDetailsRequest
Endpoint is the component that receives the request, initiates the processing and sends the response back.
Let’s first create a bean for storing the Student details.
/src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/soap/web/services/example/student/Student.java
package com.in28minutes.springboot.soap.web.services.example.student;
public class Student {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String passportNumber;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(Long id, String name, String passportNumber) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.passportNumber = passportNumber;
}
public Student(String name, String passportNumber) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.passportNumber = passportNumber;
}
// Getters and Setters omitted
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("Student [id=%s, name=%s, passportNumber=%s]", id, name, passportNumber);
}
}
/src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/soap/web/services/example/student/StudentDetailsEndpoint.java
package com.in28minutes.springboot.soap.web.services.example.student;
import org.springframework.ws.server.endpoint.annotation.Endpoint;
import org.springframework.ws.server.endpoint.annotation.PayloadRoot;
import org.springframework.ws.server.endpoint.annotation.RequestPayload;
import org.springframework.ws.server.endpoint.annotation.ResponsePayload;
import com.in28minutes.students.GetStudentDetailsRequest;
import com.in28minutes.students.GetStudentDetailsResponse;
import com.in28minutes.students.StudentDetails;
@Endpoint
public class StudentDetailsEndpoint {
@PayloadRoot(namespace = "http://in28minutes.com/students", localPart = "GetStudentDetailsRequest")
@ResponsePayload
public GetStudentDetailsResponse processCourseDetailsRequest(@RequestPayload GetStudentDetailsRequest request) {
GetStudentDetailsResponse response = new GetStudentDetailsResponse();
StudentDetails studentDetails = new StudentDetails();
studentDetails.setId(request.getId());
studentDetails.setName("Adam");
studentDetails.setPassportNumber("E1234567");
response.setStudentDetails(studentDetails);
return response;
}
}
Few important things to note:
@Endpoint- Annotation to indicate that this is a Web Service Endpoint.@PayloadRoot(namespace = "http://in28minutes.com/students", localPart = "GetStudentDetailsRequest")- Defines the details of the request that this method would handle. We will handleGetStudentDetailsRequestwith the given namespace.@ResponsePayload- This method will return a response which would need to be converted to a response xml.public GetStudentDetailsResponse processCourseDetailsRequest(@RequestPayload GetStudentDetailsRequest request)- Method would handle the request.@RequestPayloadindicates that this is got from the request.
Configure the Message Dispatcher Servlet to receive the request
/src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/soap/web/services/example/WebServiceConfig.java
@EnableWs
@Configuration
public class WebServiceConfig {
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean messageDispatcherServlet(ApplicationContext context) {
MessageDispatcherServlet messageDispatcherServlet = new MessageDispatcherServlet();
messageDispatcherServlet.setApplicationContext(context);
messageDispatcherServlet.setTransformWsdlLocations(true);
return new ServletRegistrationBean(messageDispatcherServlet, "/ws/*");
}
}
Notes
@EnableWs- Enable SOAP Web Service features in this Spring Boot application.@Configuration- This class contains Apring configuration.@Bean public ServletRegistrationBean messageDispatcherServlet(ApplicationContext context)- We would want to create message dispatcher servlet to act as a front controller.return new ServletRegistrationBean(messageDispatcherServlet, "/ws/*")- Configure the URL to the web services.
Spring Web Services Configuration to Generate WSDL
Lets add the wsdl4j dependency to our pom.xml.
/pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>wsdl4j</groupId>
<artifactId>wsdl4j</artifactId>
</dependency>
Let’s enhance the WebServiceConfig to expose the WSDL.
/src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/soap/web/services/example/WebServiceConfig.java
@Bean(name = "students")
public DefaultWsdl11Definition defaultWsdl11Definition(XsdSchema studentsSchema) {
DefaultWsdl11Definition definition = new DefaultWsdl11Definition();
definition.setPortTypeName("StudentPort");
definition.setTargetNamespace("http://in28minutes.com/students");
definition.setLocationUri("/ws");
definition.setSchema(studentsSchema);
return definition;
}
@Bean
public XsdSchema studentsSchema() {
return new SimpleXsdSchema(new ClassPathResource("student-details.xsd"));
}
Notes
@Bean(name = "students")- A spring bean. The name of the bean is the name of the wsdl in the URL.DefaultWsdl11Definition defaultWsdl11Definition(XsdSchema studentsSchema)definition.setTargetNamespace("http://in28minutes.com/students")- Default name spacedefinition.setLocationUri("/ws")- The url where we want to expose the wsdl at.definition.setSchema(studentsSchema)- We would create WSDL based on the xsd defined here -new SimpleXsdSchema(new ClassPathResource("student-details.xsd"))
URL of the WSDL - http://localhost:8080/ws/students.wsdl
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?><wsdl:definitions xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/" xmlns:sch="http://in28minutes.com/students" xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/" xmlns:tns="http://in28minutes.com/students" targetNamespace="http://in28minutes.com/students">
<wsdl:types>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified" targetNamespace="http://in28minutes.com/students">
<xs:element name="GetStudentDetailsRequest">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="id" type="xs:int"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="GetStudentDetailsResponse">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="StudentDetails" type="tns:StudentDetails"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:complexType name="StudentDetails">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="id" type="xs:int"/>
<xs:element name="name" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="passportNumber" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>
</wsdl:types>
<wsdl:message name="GetStudentDetailsResponse">
<wsdl:part element="tns:GetStudentDetailsResponse" name="GetStudentDetailsResponse">
</wsdl:part>
</wsdl:message>
<wsdl:message name="GetStudentDetailsRequest">
<wsdl:part element="tns:GetStudentDetailsRequest" name="GetStudentDetailsRequest">
</wsdl:part>
</wsdl:message>
<wsdl:portType name="StudentPort">
<wsdl:operation name="GetStudentDetails">
<wsdl:input message="tns:GetStudentDetailsRequest" name="GetStudentDetailsRequest">
</wsdl:input>
<wsdl:output message="tns:GetStudentDetailsResponse" name="GetStudentDetailsResponse">
</wsdl:output>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:portType>
<wsdl:binding name="StudentPortSoap11" type="tns:StudentPort">
<soap:binding style="document" transport="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http"/>
<wsdl:operation name="GetStudentDetails">
<soap:operation soapAction=""/>
<wsdl:input name="GetStudentDetailsRequest">
<soap:body use="literal"/>
</wsdl:input>
<wsdl:output name="GetStudentDetailsResponse">
<soap:body use="literal"/>
</wsdl:output>
</wsdl:operation>
</wsdl:binding>
<wsdl:service name="StudentPortService">
<wsdl:port binding="tns:StudentPortSoap11" name="StudentPortSoap11">
<soap:address location="http://localhost:8080/ws"/>
</wsdl:port>
</wsdl:service>
</wsdl:definitions>
Executing Request using Wizdler
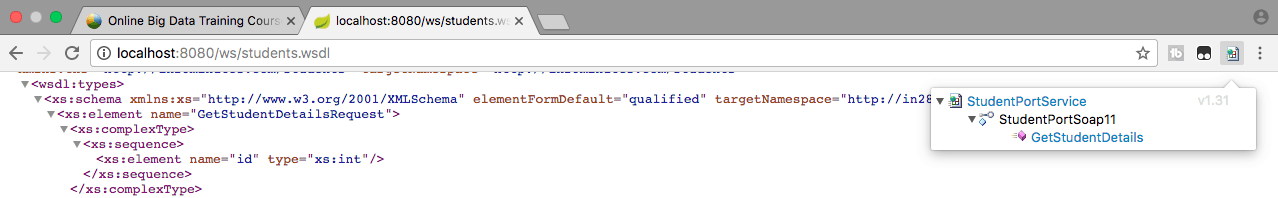
Install the chrome plugin Wizdler.
Once you install wizdler and launch the wsdl url http://localhost:8080/ws/students.wsdl, you would see a small icon at the corner of the chrome browser, which you can click to see the services that are part of the wsdl. Go ahead and click the Wizdler icon and click the service GetStudentDetails

This would launch a window to execute the request. Change the id to 1. Click Go button at the top right corner of the screen.
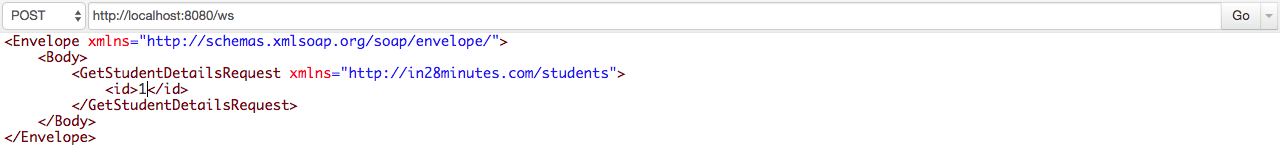
You should see the response as shown below.
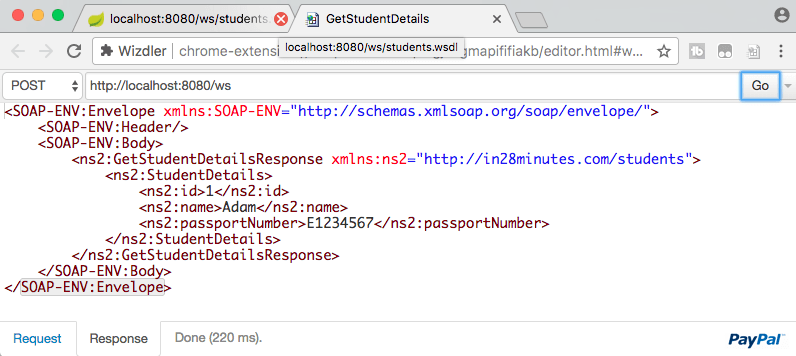
Request
<Envelope xmlns="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<Body>
<GetStudentDetailsRequest xmlns="http://in28minutes.com/students">
<id>1</id>
</GetStudentDetailsRequest>
</Body>
</Envelope>
Response
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<SOAP-ENV:Header/>
<SOAP-ENV:Body>
<ns2:GetStudentDetailsResponse xmlns:ns2="http://in28minutes.com/students">
<ns2:StudentDetails>
<ns2:id>1</ns2:id>
<ns2:name>Adam</ns2:name>
<ns2:passportNumber>E1234567</ns2:passportNumber>
</ns2:StudentDetails>
</ns2:GetStudentDetailsResponse>
</SOAP-ENV:Body>
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
More SOAP Methods
You can enhance the endpoint to expose more operations. The steps would be
- Define the structure for Request and Response in XSD
- Enhance the Endpoint to process the Request
- Go ahead and test it.
Other thing you can work on is to remove the hardcoding and add business logic and persistence stuff using JPA.
Good Luck!
Complete Maven Project With Code Examples
Our Github repository has all the code examples - https://github.com/in28minutes/spring-boot-examples/tree/master/spring-boot-tutorial-soap-web-services