Let’s learn the basics of microservices and microservices architectures. We will also start looking at a basic implementation of a microservice with Spring Boot. We will create a couple of microservices and get them to talk to each other using Eureka Naming Server and Ribbon for Client Side Load Balancing.
Here is the Microservice Series Outline: Microservices with Spring Boot
- Part 1 - Getting Started with Microservices Architecture
- Current Part - Part 2 - Creating Forex Microservice
- Part 3 - Creating Currency Conversion Microservice
- Part 4 - Using Ribbon for Load Balancing
- Part 5 - Using Eureka Naming Server
This is part 2 of this series. In this part, we will focus on creating the Forex Microservice.
You will learn
- How to create a microservice with Spring Boot?
- How to create a JPA Entity and Resource?
- How to get Spring MVC, Spring Boot, JPA, Hibernate and H2 to work together?
Resources Overview
Forex Service (FS) is the Service Provider. It provides currency exchange values for various currency. Let’s assume that it talks to a Forex Exchange and provides the current conversion value between currencies.
An example request and response is shown below:
GET to http://localhost:8000/currency-exchange/from/EUR/to/INR
{
id: 10002,
from: "EUR",
to: "INR",
conversionMultiple: 75,
port: 8000,
}
The request above is the currency exchange value for EUR to INR. In the response, conversionMultiple is 75.
Project Code Structure
Following screenshot shows the structure of the project we will create.
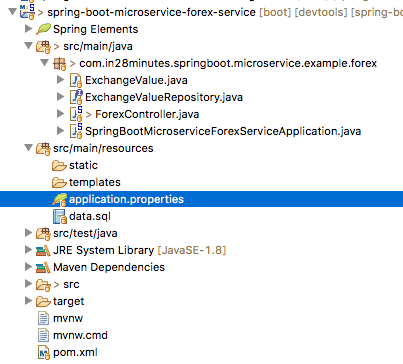
A few details:
- SpringBootMicroserviceForexServiceApplication.java - The Spring Boot Application class generated with Spring Initializer. This class acts as the launching point for application.
pom.xml- Contains all the dependencies needed to build this project. We will use Spring Boot Starter Web and JPA.ExchangeValue.java- Exchange Value EntityExchangeValueRepository.java- ExchangeValue JPA Repository. This is created using Spring Data JpaRepository.ForexController.java- Spring Rest Controller exposing the forex conversion service.- data.sql - Initial data for the exchange_value table. Spring Boot would execute this script after the tables are created from the entities.
Tools you will need
- Maven 3.0+ is your build tool
- Your favorite IDE. We use Eclipse.
- JDK 1.8+
Complete Maven Project With Code Examples
Our Github repository has all the code examples - https://github.com/in28minutes/spring-boot-examples/tree/master/spring-boot-basic-microservice
Bootstrapping with Spring Initializr
Creating a Microservice with Spring Initializr is a cake walk.
Spring Initializr http://start.spring.io/ is great tool to bootstrap your Spring Boot projects.
You can create a wide variety of projects using Spring Initializr.

Following steps have to be done for a Web Services project
- Launch Spring Initializr and choose the following
- Choose
com.in28minutes.springboot.microservice.example.forexas Group - Choose
spring-boot-microservice-forex-serviceas Artifact - Choose following dependencies
- Web
- DevTools
- Starter JPA
- H2
- Choose
- Click Generate Project.
- Import the project into Eclipse. File -> Import -> Existing Maven Project.
Creating Exchange Value Entity
@Entity
public class ExchangeValue {
@Id
private Long id;
@Column(name="currency_from")
private String from;
@Column(name="currency_to")
private String to;
private BigDecimal conversionMultiple;
private int port;
public ExchangeValue() {
}
public ExchangeValue(Long id, String from, String to, BigDecimal conversionMultiple) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.conversionMultiple = conversionMultiple;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public String getFrom() {
return from;
}
public String getTo() {
return to;
}
public BigDecimal getConversionMultiple() {
return conversionMultiple;
}
public int getPort() {
return port;
}
public void setPort(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
}
Important things to note:
@Entity: Specifies that the class is an entity. This annotation is applied to the entity class.@Id: Specifies the primary key of an entity.
Creating Exchange Value JPA Repository
/spring-boot-microservice-forex-service/src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/microservice/example/forex/ExchangeValueRepository.java
package com.in28minutes.springboot.microservice.example.forex;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface ExchangeValueRepository extends
JpaRepository<ExchangeValue, Long>{
ExchangeValue findByFromAndTo(String from, String to);
}
Notes
public interface ExchangeValueRepository extends JpaRepository<ExchangeValue, Long>- We are extending JpaRepository using two generics - ExchangeValue & Long. ExchangeValue is the entity that is being managed and the primary key of ExchangeValue is Long.ExchangeValue findByFromAndTo(String from, String to);- We would want to query the conversion value from one currency to another. We are defining a query method for it.
Create the Resource - ForexController
/spring-boot-microservice-forex-service/src/main/java/com/in28minutes/springboot/microservice/example/forex/ForexController.java
@RestController
public class ForexController {
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@Autowired
private ExchangeValueRepository repository;
@GetMapping("/currency-exchange/from/{from}/to/{to}")
public ExchangeValue retrieveExchangeValue
(@PathVariable String from, @PathVariable String to){
ExchangeValue exchangeValue =
repository.findByFromAndTo(from, to);
exchangeValue.setPort(
Integer.parseInt(environment.getProperty("local.server.port")));
return exchangeValue;
}
}
Notes
@RestController public class ForexController {- Create a Controller to expose a Rest Service@Autowired private Environment environment- We would want to return the server port back. This will help us identify which instance service is giving the response back.@Autowired private ExchangeValueRepository repository- Autowire the repository.ExchangeValue exchangeValue = repository.findByFromAndTo(from, to)- Get the exchange value from the database.exchangeValue.setPort(Integer.parseInt(environment.getProperty("local.server.port")))- Get the port from environment and set it into the response bean.
Configure Application Name and a few other configuration
/spring-boot-microservice-forex-service/src/main/resources/application.properties
spring.application.name=forex-service
server.port=8000
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb
spring.data.jpa.repositories.bootstrap-mode=default
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
We are assigning a port of 8000 for this application and enabling debug logging.
Insert some test data into data.sql
Let’s insert some test data by creating a file called data.sql. Spring Boot Auto Configuration ensures that this data is loaded up when application starts up.
/spring-boot-microservice-forex-service/src/main/resources/data.sql
insert into exchange_value(id,currency_from,currency_to,conversion_multiple,port)
values(10001,'USD','INR',65,0);
insert into exchange_value(id,currency_from,currency_to,conversion_multiple,port)
values(10002,'EUR','INR',75,0);
insert into exchange_value(id,currency_from,currency_to,conversion_multiple,port)
values(10003,'AUD','INR',25,0);
Test Forex Microservice
GET to http://localhost:8000/currency-exchange/from/EUR/to/INR
{
id: 10002,
from: "EUR",
to: "INR",
conversionMultiple: 75,
port: 8000,
}
Next Steps
Microservices with Spring Boot
- Part 1 - Getting Started with Microservices Architecture
- Current Part - Part 2 - Creating Forex Microservice
- Part 3 - Creating Currency Conversion Microservice
- Part 4 - Using Ribbon for Load Balancing
- Part 5 - Using Eureka Naming Server